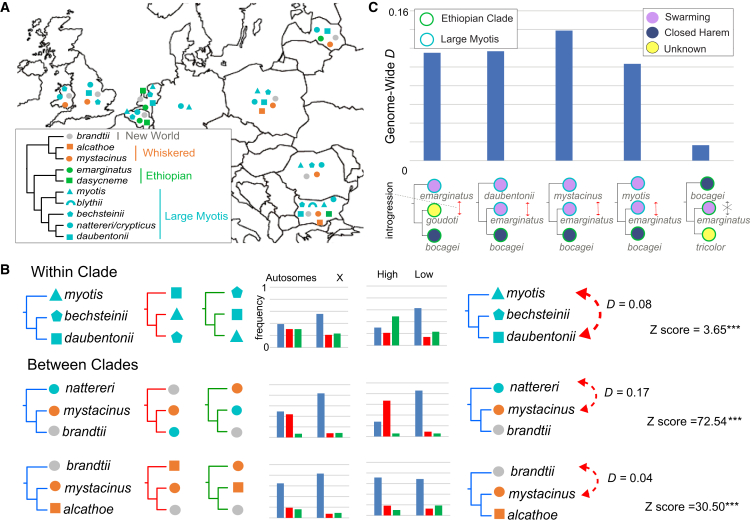
Figure 5.
Introgression occurs among species that co-occur at swarming sites
(A) Species assemblages reported at swarming sites throughout Europe (Table S6). The tree inset shows the species tree and clade membership of each species.
(B) Examples of within and between clade introgression. Variation in topological frequency is observed between autosomal, X, and high and low recombining genomic partitions. Whole--genome D-statistics demonstrate phylogenomic conflict is due to introgression.
(C) Comparisons of the genome-wide D-statistic for species representing the large myotis clade, with a promiscuous mating system, and M. bocagei from the Ethiopian clade, which employs a conservative (closed harem) mating system. The same analysis was repeated using M. yumanensis as the reference genome to demonstrate that our results are not confounded by reference bias (Figure S25; Table S5). Trees for introgression tests are represented top to bottom in the format (H1, (H2, H3)), O), where the outgroup O (S. latirostris) is not shown. See Table S5 for detailed results.