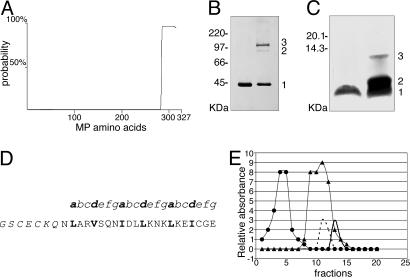
Fig. 2.
Analysis of CaMV MP structure. (A) Computer prediction of coiled-coil domains within the MP sequence. The entire MP protein is represented on the x axis and coiled-coil probability (%) on the y axis. (B) Chemical cross-linking of MP analyzed by SDS/PAGE and detected by immunoblot analysis with anti-MP coiled-coil antibody. Positions of the monomer and the cross-linked dimers and trimers (1, 2, and 3, respectively) are indicated [CaMV MP (37 kDa) migrates anomalously on SDS/PAGE, ref. 21]. The product in the left lane was not treated with Bis 2-sulfosuccinimidooxycarbonyloxyethylsulfone. (C) Disulfide cross-linking of CoilMP analyzed by oxidative SDS/PAGE and silver staining. Positions of the peptide monomer and cross-linked dimers and trimers (1 = 3,235 Da, 2 = 6,470 Da, and 3 = 9,705 Da) are indicated. The product in the left lane was not treated with oxidized glutathione. (D) Synthetic peptide CoilMP, corresponding to the C-terminal α-helical domain of MP (nonnative amino acids in italics), with the seven amino acid unit (depicted as a-g) of the heptad repeat structure illustrated above; hydrophobic residues of the α-helix occupy positions a and d (highlighted in bold). (E) Separation of reduced CoilMP(wt) by gel filtration on Superdex 200 (Amersham Pharmacia). Standard molecular mass markers are chymotrypsinogen A (25 kDa, •) and cytochrome c (12.4 kDa, ▴). The elution peaks correspond to CoilMP(wt) peptide trimer (7,155 Da, solid black line), and CoilVAP(wt) peptide tetramer (16,596 Da, dashed black line). Protein concentration was determined by monitoring absorbance at 280 nm of each 0.5-ml elution fraction.