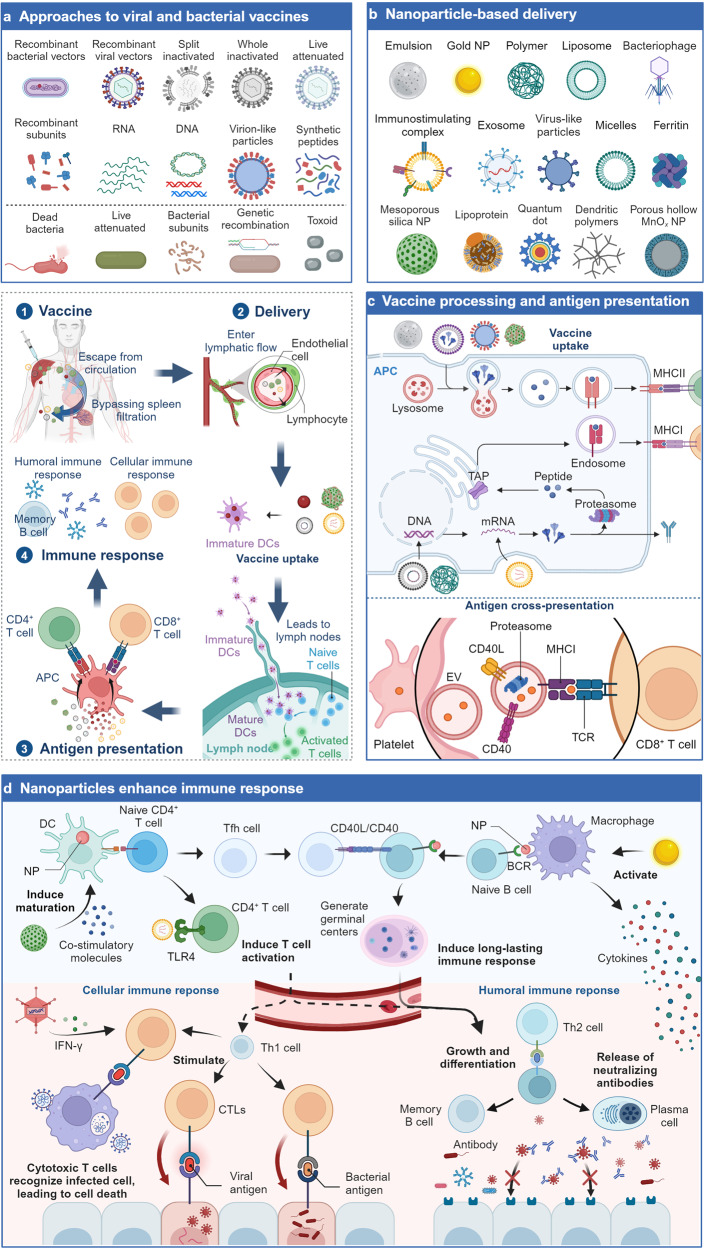
Fig. 2.
The application of NPs-based vaccines for pathogen prevention. After vaccination, due to the small size of the NP carrier, the nano-vaccines are more likely to escape from the bloodstream, bypass splenic filtration, enter the lymphatic flow, and then be absorbed by immature DCs, together with DCs, enter the lymph nodes, and initiate a series of immune reactions. a Types and methods for the production of viral and antibacterial vaccines. b Various nanomaterials used for antigen delivery. c Mechanisms of NP entry into cells and antigen presentation. d Mechanisms by which NPs enhance immune responses. NPs have diverse stimulating effects on the immune system, including inducing the production of co-stimulatory molecules to induce DCs maturation;795,796 promoting strong T cell activation;276 facilitating germinal center formation to induce long-lasting effective immune responses;797 and stimulating macrophages to produce cytokines to enhance immune responses.798 ①–④. The immune process of NP-based vaccines. TAP: transporter associated with antigen processing; Tfh: T follicular helper; Th2: T helper-2 cell; CTLs: cytotoxic T lymphocytes