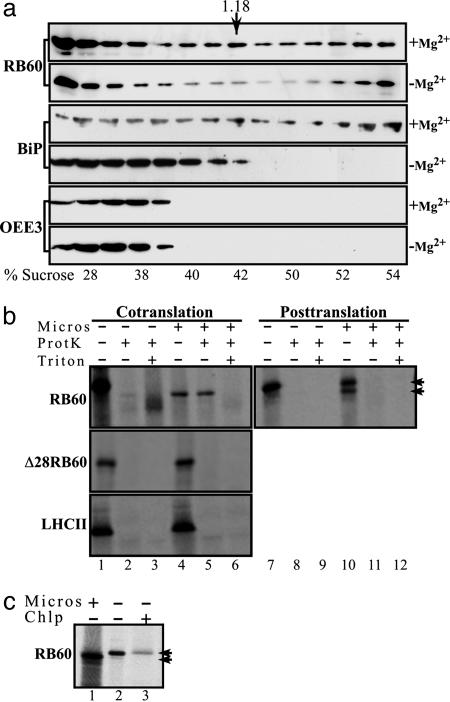
Fig. 2.
Biochemical evidence of the ER localization and independent import of RB60. (a) RB60 is found in microsomes of C. reinhardtii. Sucrose gradient fractionation of cytoplasmic extracts of C. reinhardtii cells was performed in the presence (+Mg2+) or the absence (-Mg2+) of Mg2+, followed by immunoblot analysis using anti-RB60 (RB60) or anti-BiP (BiP) sera or sera raised against the chloroplast OEE3 protein (OEE3). Similarly to BiP, the peak of RB60 bands at a density of ≈1.18 g·ml-1 (the density of peak fraction of rough ER, denoted by an arrow), and in a magnesium shift assay, an established test for microsomes of the rough ER, the peaks of RB60 and BiP displayed a similar shift to the lighter sucrose fractions. The actual sucrose density of each fraction is denoted below each lane (% sucrose). (b) RB60 imports cotranslationally into microsomes. Cotranslational translocation (Cotranslation) into dog pancreas microsomes was performed with in vitro synthesized, 35S-labeled RB60 (RB60), a leaderless RB60 (Δ28RB60), and LHCII (LHCII) recombinant proteins in the presence of microsomes (Micros) as indicated above the lanes. For posttranslational assays (Posttranslation), 35S-labeled proteins were first synthesized in vitro in the absence of microsomes. Protease-protected microsomal translocation was ensured by proteinase K treatment (ProtK). Treatment with Triton X-100 (Triton) verified that the proteinase K-treated proteins were indeed taken up by microsomes. The two arrowheads indicate the migration of the precursor and cleaved forms of RB60. (c) In contrast to the chloroplast, the leader of RB60 is cleaved after uptake by microsomes. In-vitro-synthesized, 35S-labeled RB60 (lane 2) was separated by using SDS/PAGE alongside RB60 imported by dog pancreas microsomes (lane 1) and chloroplast-imported RB60 (lane 3).