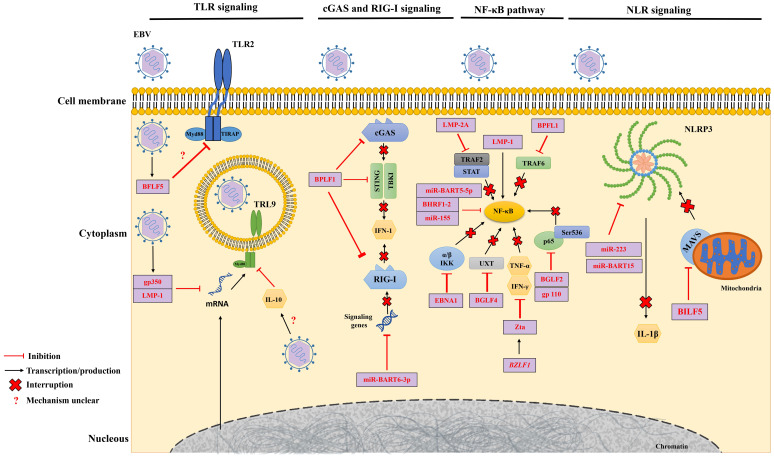
Figure 2.
EBV-Mediated Mechanisms of Immune Evasion. EBV evades the immune response by interfering with key molecular pattern receptors (PRRs) and the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway. EBV molecules, proteins and miRNAs play roles in suppressing the activity of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) (left), cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) and retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) (center left), in the NF-κB pathway (center right) and the NOD-like receptor (NLR) (right). Furthermore, EBV disrupts the production of products resulting from these pathways, directly or indirectly.