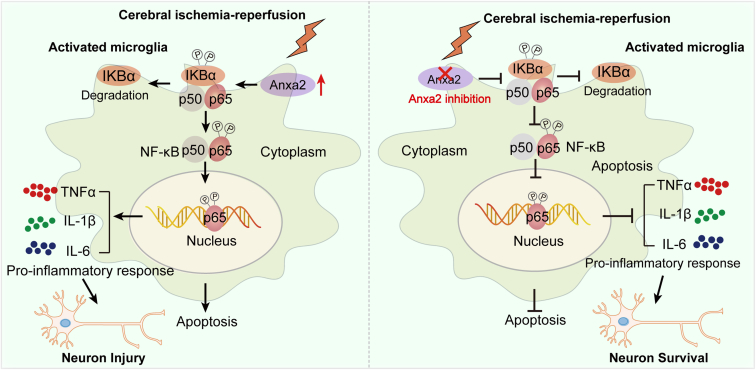
Fig. 8.
Graphical illustration of the potential molecular mechanism of the Anxa2 gene in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Anxa2 in microglia is activated following ischemia-reperfusion; upregulation of Anxa2 expression can activate the NF-κB signaling pathway through nuclear translocation of NF-κB. Activated Anxa2 promotes the NF-κB pathway, which promotes the transcription activity of NF-κB, thus promoting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and cell apoptosis, thereby promoting subsequent neuronal death; Anxa2 suppression can alleviate OGD/R-induced inflammatory response and apoptosis by inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway and the expression of its downstream pro-inflammatory genes, thereby preventing subsequent neuronal death. Anxa2, annexin A2; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; OGD/R, oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation.