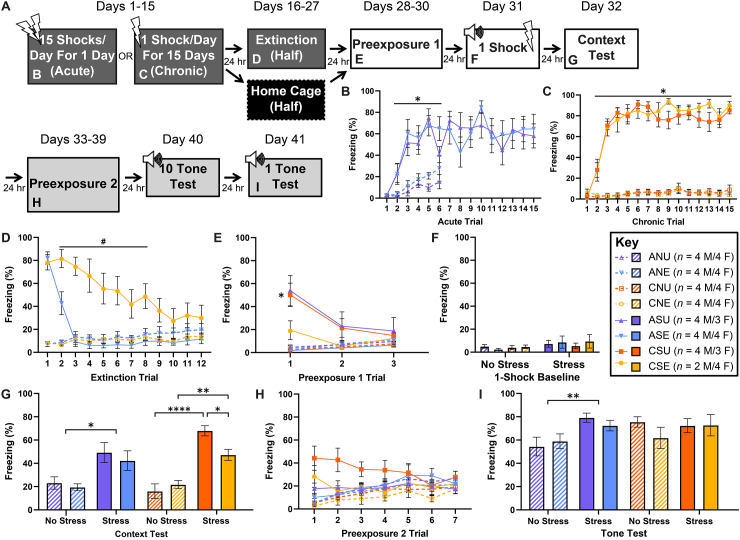
Fig. 3.
Effects of stressor context fear extinction on subsequent contextual and auditory fear learning. Depicted: Schematic illustration of the experiment timeline and the figure panels in which data from the experiment are displayed (panel A). Percent freezing during stress pretreatment (panels B & C, days 1–15), stressor context fear extinction (panel D, days 16–27), context preexposures (panels E & H, days 28–30 and days 33–39, respectively), single-shock baseline (panel F, day 31), context test (panel G, day 32), and tone test (panel I, day 41). Rats received either acute (AS) or chronic (CS) exposure to 15 footshocks, or identical context exposure with no shock (No Stress; AN/CN). Following stress pretreatment, rats received (E) or did not receive (U) extinction training to the stressor context. Following extinction training, all rats were preexposed to a novel context (30 min/day) for 3 consecutive days. Twenty-four hours after preexposure, all groups received a single footshock in the preexposed context. All groups were tested for contextual fear learning 24 h later, then preexposed to a third context (30 min/day) for 7 days, and, finally, tested for fear conditioning to the tone in this context. Rats that received chronic stress exhibited a slower rate of extinction (panel D). CSU rats exhibited higher levels of fear expression to the novel context (panel E). All groups displayed comparably low baseline levels of fear prior to the single-shock exposure (panel F). Stressed rats exhibited enhanced fear learning to the single-shock session. However, extinction training attenuated learning only in the chronic-stress group (panel G). Furthermore, only AS groups exhibited enhanced fear learning to the tone (panel I). Error bars denote mean ± SEM. *, **, and **** denotes significance (p ≤ .05, p ≤ .01, and p ≤ .0001, respectively) compared between indicated groups (horizontal square brackets), compared between each Stress group and its respective No Stress control (horizontal line), or compared between a specific Stress group and its respective No Stress control (free-standing). # denotes significance (p ≤ .05) compared between CSE and ASE (horizontal line).