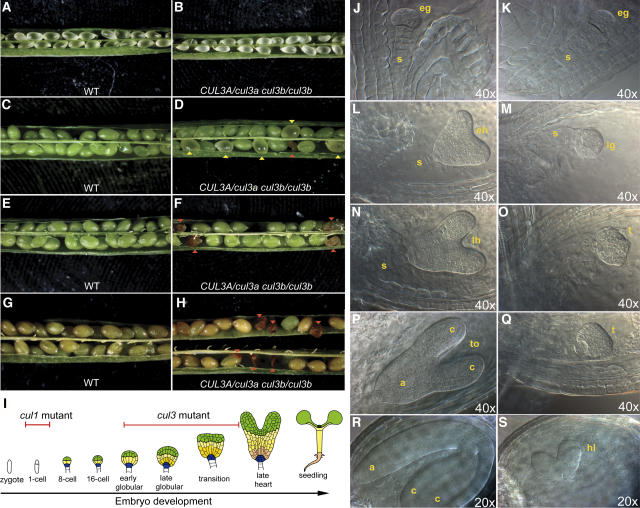
Figure 2.
Loss of Function in Both Arabidopsis CUL3 Genes Causes Arrest in Embryogenesis.
(A) and (B) Stereomicroscopic images of siliques obtained from self-pollinated wild-type (WT [A]) or CUL3A/cul3a cul3b/cul3b (B) parental plants at an early developmental stage, when wild-type embryos are at the transition between the globular and heart stages.
(C) and (D) Stereomicroscopic images of siliques obtained from self-pollinated wild-type (C) or CUL3A/cul3a cul3b/cul3b (D) parental plants at a later developmental stage, when wild-type embryos are at the mature stage. Yellow arrowheads indicate pale green/yellow ovules containing arrested embryos. Red arrowheads indicate red shrunken ovules.
(E) to (H) Stereomicroscopic images of siliques obtained from self-pollinated wild-type ([E] and [G]) or CUL3A/cul3a cul3b/cul3b ([F] and [H]) parental plants during the onset of seed maturation. Red arrowheads in (F) and (H) indicate the pale green/yellow ovules (described in [D]) that turned into shrunken seeds.
(I) Scheme of Arabidopsis embryo development, adapted from Laux et al. (2004). Red bars indicate the stages of arrest of Arabidopsis cul1 and cul3 mutant embryos.
(J) to (S) DIC images of cleared ovules obtained from the self-pollination of CUL3A/cul3a cul3b/cul3b parental plants. At an early developmental stage (early globular; [J] and [K]), all of the embryos are uniformly developed. Starting from the transition between the late globular and torpedo stages, the cul3a cul3b embryos arrest at late globular/transition stages ([M], [O], and [Q]), whereas the sibling embryos ([L], [N], and [P]) from the same siliques proceed from globular, to heart, to torpedo, to mature embryos. Occasionally, cul3a cul3b embryos were arrested at a heart-like stage (S).
a, axis; c, cotyledons; eg, early globular-stage embryo; eh, early heart-stage embryo; hl, heart-like embryo; lg, late globular-stage embryo; lh, late heart-stage embryo; s, suspensor; t, transition-stage embryo; to, torpedo-stage embryo.