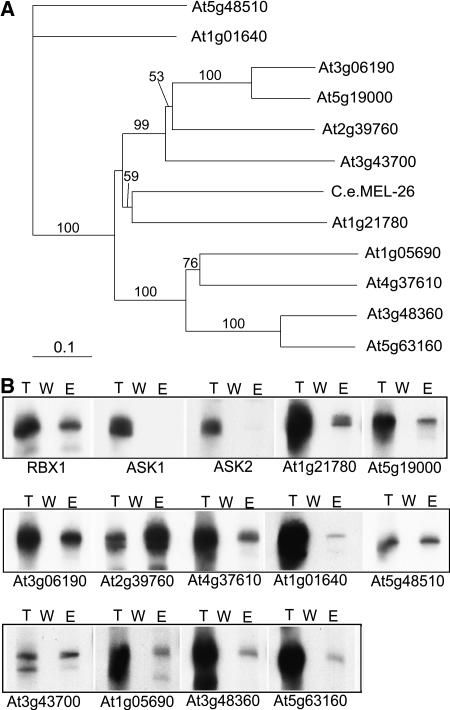
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic Comparison of 11 Cloned BTB Protein Genes and Their in Vitro Binding to AtCUL3.
(A) Phylogenetic analysis of the BTB domains in several Arabidopsis proteins. Sequence data for the proteins used in the phylogenetic analysis were taken from the EMBL/GenBank databases using the following accession numbers: At1g21780 (AAM65090), At5g19000 (AAM97116), At3g06190 (AAF30312), At2g39760 (NP_030522), At4g37610 (AAN15363), At1g01640 (AAF78396), At5g48510 (NP_199662), At3g43700 (CAB83071), At1g05690 (AAQ87006), At3g48360 (AAN31824), At5g63160 (AAR24650), and C. elegans MEL-26 (NP_492449). Sequence alignment of the BTB protein families was conducted using ClustalX (version 1.83) software (Thompson et al., 1997). The Gonnet protein weight matrices (Gonnet 40, 80, 120, 160, 250, and 350 matrices [Gonnet et al., 1992]) were selected, and the gap-opening and extension parameters were 10 and 0.2, respectively. Distance (mean standard distance) phylogenetic analysis was performed in PAUP 4.0 (score 3.41; Swofford, 2000). Bootstrap support (Felsenstein, 1985) for nodes was estimated using 1000 replicates under mean standard distance.
(B) AtCUL3A interacts in vitro with several members of the Arabidopsis BTB family but not with SKP1/ASK1 or SKP1/ASK2. An in vitro pull-down assay was performed using purified MBP-AtCUL3A and in vitro–translated Arabidopsis BTB proteins. Lane T, total in vitro–translated BTB protein; lane W, the last wash before elution; lane E, the protein eluted.