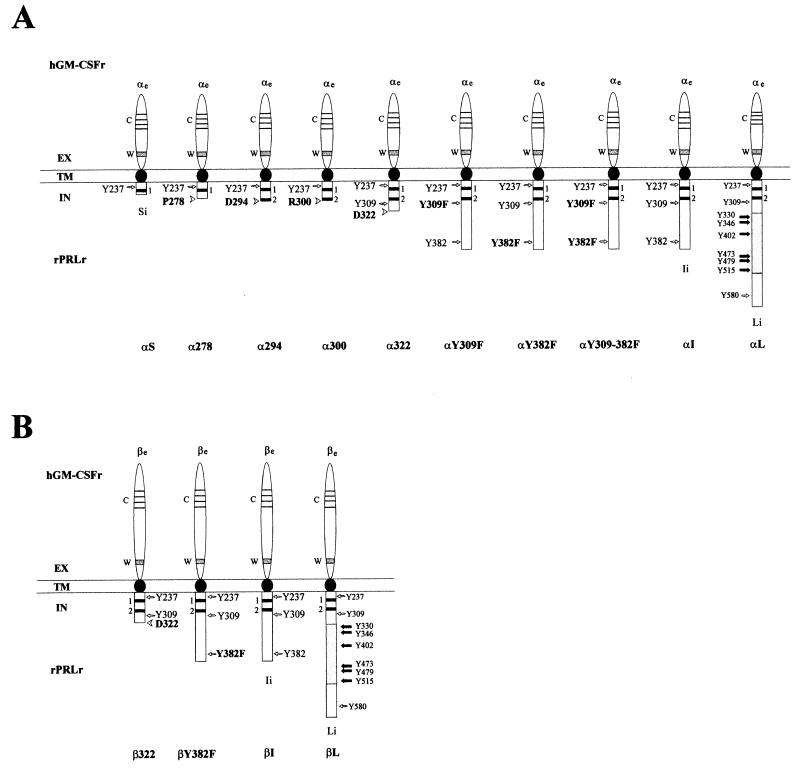
FIG. 1.
Schematic representation of the chimeric GM-CSFr/PRLr. The extracellular, transmembrane, and intracellular domains are abbreviated as EX, TM, and IN, respectively. The chimeric receptors consisted of the extracellular domain of the hGM-CSFr α or β subunit, termed αe or βe and the transmembrane and intracellular domains of the rat PRLr-S (rPRLr-S) PRLr-I, or PRLr-L isoforms, termed Si, Ii, or Li, respectively. Syntheses of chimera between αe or βe and Si, Ii, or Li were termed αS, αI, αL, βI, or βL, respectively. Mutations of αI termed α278, α294, α300, or α322 represented truncations immediately C terminal to the V box, a partial box 2, a full-length box 2, and the X box, respectively. A single truncation to βI, termed β322, was also synthesized. Replacements of the tyrosines with phenylalanine at residue 309 or 382 were respectively termed αY309F, αY382F, αY309+382F, or βY382F. The conserved extracellular domain regions including the four cysteine residues and a WSXWS motif are respectively indicated by C and W. Two thick lines labeled 1 and 2 indicate the conserved box 1 and box 2 motifs.