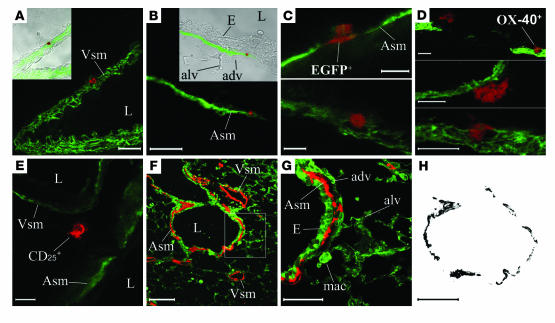
Figure 2.
Confocal microscopy. (A–E) Distribution of EGFP+ (A–C), OX-40+ (D), and CD25+ (E) cells (red signal) relative to α-SMA (green signal). Insets in A and B show an overlay of the confocal sections over transmission histological images. (A) Example of an EGFP+ cell inside vascular smooth muscle (Vsm), likely exiting a small vessel (L, lumen). (B–D) Confocal colocalization in 0.6-μm-thick optical sections suggesting direct contact between EGFP+ (B and C) or OX-40+ (D) cells and ASM (Asm). adv, adventitia; alv, alveolar walls; E, bronchial epithelium. (E) A CD25+ cell likely migrating between a vessel and a neighboring airway. (F–H) Confocal extraction of ASM for quantitation. (F) In an airway, the smooth muscle bundles are identified by α-SMA immunostaining (red). The green signal corresponds to pan-actin (all actin isoforms), which was used as a general counterstain. (G) A high-magnification field (corresponding to the square in F) illustrates the airway epithelium, smooth muscle, adventitia, alveolar walls, and alveolar macrophages (mac). (H) The ASM bundles were isolated by confocal subtraction, to measure their surface area corrected by airway size. Scale bars: 100 μm (F and H); 50 μm (G); 20 μm (A and B); 10 μm (D and E); and 5 μm (C).