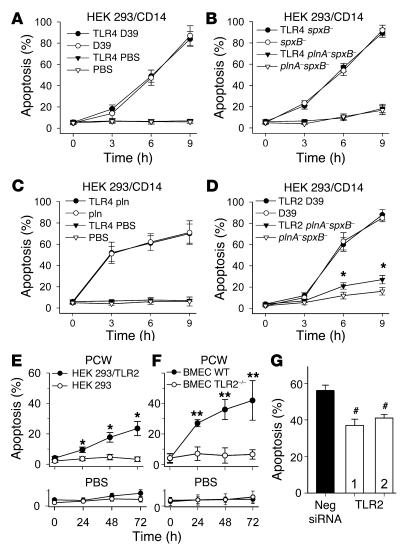
Figure 5.
Role of receptors in pneumococcal-induced PCD. (A) Pneumococci (D39) induced cell death independent of the presence of TLR4. Pneumococci deficient in H2O2 (spxB–) induced cell death as effectively as did wild-type pneumococci (D39; A and B). (B) plnA–spxB– caused significantly less PCD that was not changed by the presence of TLR4. (C) Additionally, the ability of purified pneumolysin (pln) to cause PCD was not modified by the presence of TLR4. (D) HEK 293 cells were killed by wild-type pneumococci (D39) independent of the presence of TLR2. plnA–spxB– induced significantly more PCD in HEK 293 cells transfected with TLR2 after 6 and 9 hours. All data presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, Student’s t test. (E) PCW (107 CFU equivalents) induced significantly more PCD in HEK 293 cells stably transfected with TLR2 at 24, 48, and 72 hours. *P < 0.05; Student’s t test. (F) PCW (107 CFU equivalents) caused PCD in wild-type BMECs, whereas PCW did not induce PCD in BMECs prepared from TLR2-deficient mice. **P < 0.01; Student’s t test. (G) Transfection with 2 different TLR2 siRNAs (1, TLR2-1; 2, TLR2-2) significantly reduced PCD compared with transfection with a nonsilencing RNA at 48 hours. Neg siRNA, nonsilencing control. #P < 0.001 (Student’s t test) in immortalized rat BMECs after incubation with PCW (107 CFU equivalents).