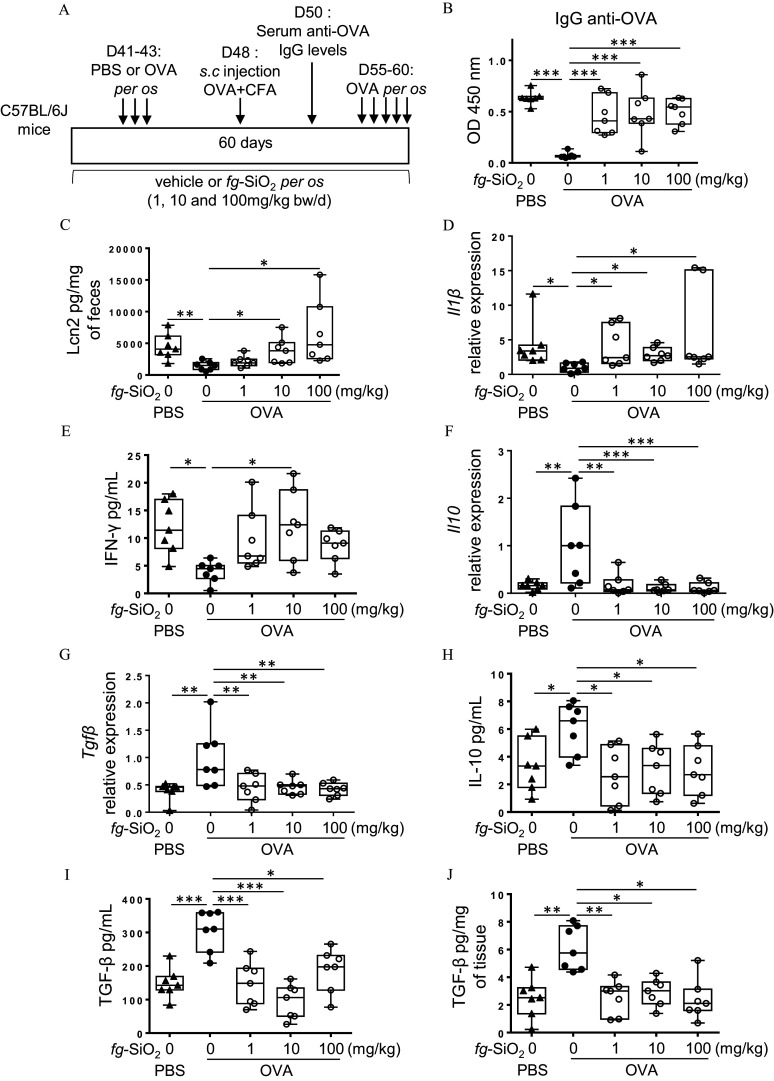
Figure 3.
Evaluation of oral tolerance and gut immune response to ovalbumin in mice exposed 60 d to food-grade . (A) The protocol of oral tolerance induction to ovalbumin (OVA) followed by a de novo challenge to OVA in C57BL/6J mice daily exposed to the vehicle (water) or to the food-grade () (1, 10, or BW/d) through gavage. (B) OVA-specific IgG secretion in OVA-immunized (PBS) or OVA-tolerized mice exposed to a vehicle or for 60 d ( mice per group). (C) Fecal lipocalin-2 (Lcn2) levels in OVA-immunized (PBS) or OVA-tolerized mice exposed to a vehicle or for 60 d ( mice per group). (D) transcript expression in colon of OVA-immunized (PBS) or OVA-tolerized mice exposed to a vehicle or for 60 d ( mice per group). (E) Amounts of secreted by mesenteric lymph node (MLN) cells from OVA-immunized (PBS) or OVA-tolerized mice exposed to a vehicle or for 60 d ( mice per group). (F,G) Il10 (F) and (G) transcript expression in colon of OVA-immunized (PBS) or OVA-tolerized mice exposed to a vehicle or for 60 d ( mice per group). (H,I) Amounts of IL-10 (H) and (I) secreted by mesenteric lymph node cells from OVA-immunized (PBS) or OVA-tolerized mice exposed to a vehicle or for 60 d ( mice per group). Secreted amounts by colon explants from OVA-immunized (PBS) or OVA-tolerized mice exposed to a vehicle or for 60 d ( mice per group). The data are expressed as median with interquartile range and whiskers extending from minimum to maximum ± SEM. *; **; *** by one-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey test (E–J) or Kruskal-Wallis test followed by a post hoc Dunn’s test (C,D). Data behind graphs are reported in Table S4. Note: ANOVA, analysis of variance; BW, body weight; CFA, complete Freund adjuvant; IgG, immunoglobulin G; , interferon gamma; IL-10, interleukin 10; OD, optical density; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; SEM, standard error of the mean; , transforming growth factor beta.