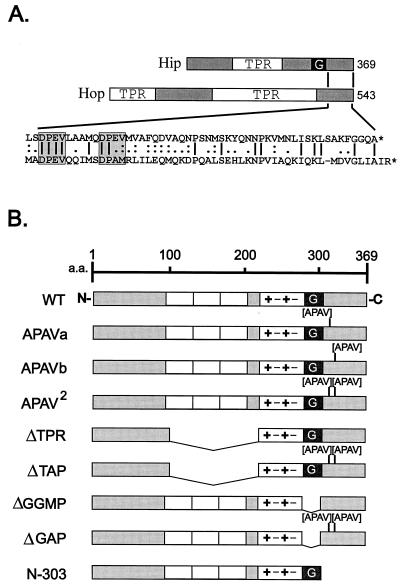
FIG. 1.
(A) Comparison of Hip and Hop sequences. Hsp70-binding proteins Hip and Hop both contain TPR domains. In Hip, the TPR domain plus surrounding highly charged sequences is required for Hsp70 binding. Also contained in Hip is a GGMP repeat domain (G) whose function is unknown. Hop contains two TPR regions; the N-terminal one is required for Hsp70 binding, and the central TPR binds to Hsp90. Little homology is shared between the highly degenerate TPR regions of Hip and Hop. The region of greatest similarity is near the C terminus of each protein (amino acid sequence alignment in exploded view at bottom). Most notable in this region are two DPEV sequences in Hip that align with a DPEV and DPAM in Hop (highlighted by shaded boxes). (B) Hip mutants. Each of the DPEV sequences in Hip was mutated to APAV, as illustrated. The mutation of both DPEV sequences (APAV2) was also combined with previously developed mutants in which the TPR or GGMP domains had been deleted. Another mutant from previous studies is the truncation mutant N-303, which lacks the DPEV-containing C terminus of Hip. TPR domains (open boxes), highly charged regions (+−+−), and a region of Hop homology (shaded box) at the C terminus are shown. a.a., amino acids; WT, wild type.