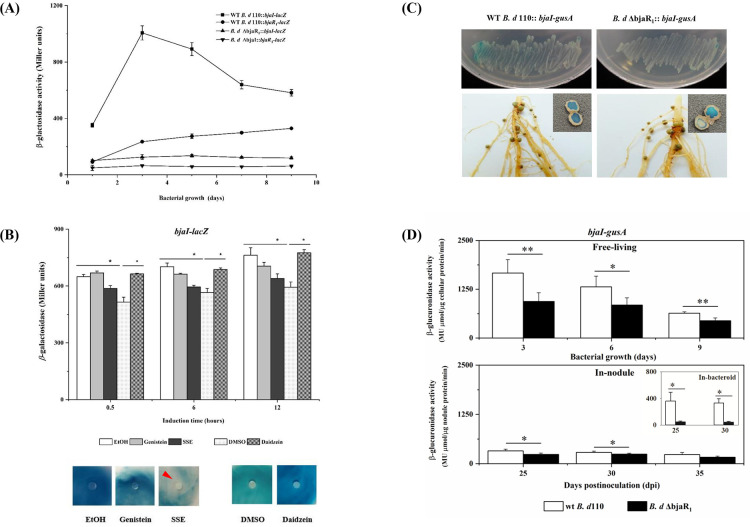
Fig 1.
(A) The promoter activity of the bjaI and bjaR1 genes in B. diazoefficiens strains grown in yeast-extract mannitol (YEM) liquid medium. The wt B. d 110 :: bjaI-lacZ or wt B. d 110 :: bjaR1-lacZ denotes strains harboring a transcriptional lacZ fusion with the promoter region of either the bjaI or bjaR1 gene in the wild-type (WT) B. diazoefficiens USDA110, while B. d ΔbjaR1::bjaI-lacZ and B. d ΔbjaI::bjaR1-lacZ are derived from corresponding mutant backgrounds. (B) The bjaI-lacZ activity in WT B. diazoefficiens USDA110 grown in liquid YEM medium (upper panel) and GUS stain (bjaI-gusA) through agar plate-sensitivity assay (lower panel). Pure isoflavonoids (i.e., genistein or daidzein) at a final concentration of 5.0 µM, as well as soybean seed extract (SSE) (20 µL/mL culture), were applied. DMSO, dimethyl sulphoxide, the solvent for daidzein. The substrates for the lacZ activity assay and GUS-staining were 13.0 mM O-nitrophenyl-D-galactopyranoside (ONPG) and 38.0 mM 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-glucronide (X-Gluc), respectively. For agar plate-sensitivity testing, the reporter bacteria suspension and X-Gluc were spread on the plate surface, while the chemical compounds were dropped on the filter paper. The red arrow indicates the inhibition zone. (C) The GUS stain in B. diazoefficiens strains grown in the YEM plate (upper panel) and nodules (lower panel) formed at 40 days post-inoculation (dpi). (D) The quantified GUS activity in bacteria growing in YEM liquid media and soybean nodule (i.e., utilizing nodule extract and bacteroid for determination). 4-methylumbelliferyl-D-glucuronide (MUG_GUS) was used as a substrate. The data represent the means ± standard errors (SEs) of six samples from two independent experiments, with statistically significant differences indicated by asterisks (* or **) (P-value ≤ 0.05 or 0.01).