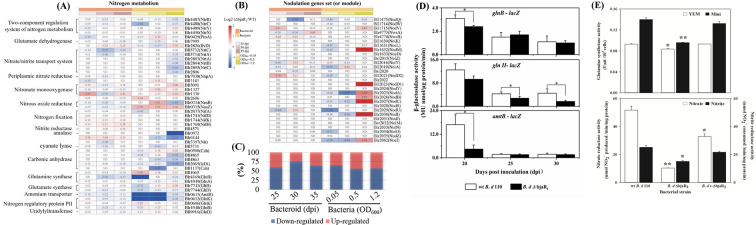
Fig 4.
The proteomic profiles of nitrogen metabolism (A) and nodulation (B) genomic module in B. diazoefficiens bacteroids formed at different days post-inoculation (dpi) and bacterial culture grown at various optical densities at 600 nm (OD600). The value within each box represents the log2 (fold change, FC) of protein abundance in ΔbjaR1 mutant compared to that in WT cells. Protein abundance is indicated as an average mass spectrometry signal for proteins from three samples determined by label-free quantification (LFQ) intensities obtained from DIA-NN output. ND indicates not detected. (C) The proportion of downregulated or upregulated proteins among all detected proteins in the nitrogen metabolism module in Fig. 4A. (D) Promoter activities of N-responsive genes in soybean root nodules formed at various days post-inoculation (dpi). The genes glnB (blr4948), glnII (blr4169), and amtB (blr0613) encode the N-regulatory protein PII, glutamine synthetase, and an ammonium transporter, respectively. Nodules from each soybean plant were collected and crushed for lacZ fusion activity assays using 4-methylumbelliferyl-β-D-galactopyranoside (MUG_LACZ) as a fluorogenic substrate. Data represent means ± SEs of six plants across two independent experiments. (E) Glutamine synthetase activity in B. diazoefficiens cells grown in YEM and minimal (Mini) liquid media (38). One unit of enzyme activity is defined as a change of 0.01 in the OD540 value per minute for every 104 cells. The data presented are the means ± SEs of six samples from two independent experiments. Nitrate/nitrite reductase activity was determined in anaerobically grown B. diazoefficiens cells after 4 days in a YEM liquid medium containing 10 mM KNO3. Asterisks (*or**) denote statistically significant differences compared to the WT strain, with a P-value ≤ 0.05 or 0.01 significance level.