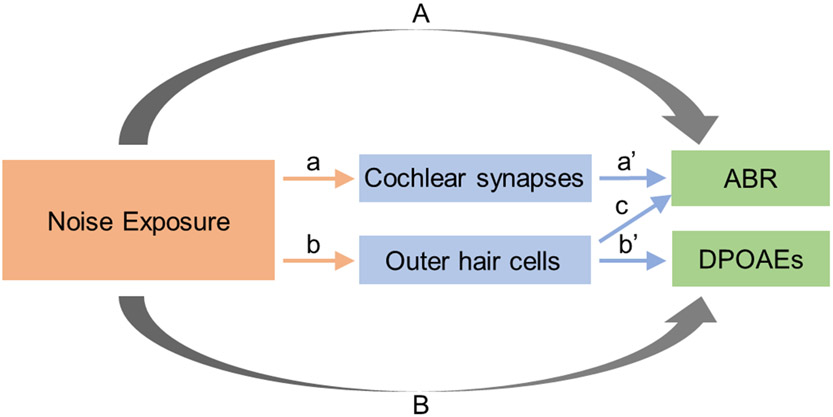
Figure 3. Schematic demonstrating the concept of post-treatment bias.
Noise exposure is assumed to impact both cochlear synapses (a) and OHCs (b). Cochlear synaptic function is measured using the ABR (a’) and OHC function using DPOAEs (b’). To assess the impact of noise exposure on cochlear synapses, we evaluate the effect of noise exposure on the ABR (A). OHC function may alter the ABR (c), but if we try to adjust out the impact of OHC function on the ABR by including DPOAEs as a predictor in our regression model, we may also be adjusting out the noise exposure effect on the ABR (A) because noise exposure also impacts DPOAEs (B). This problem is referred to as post-treatment bias.