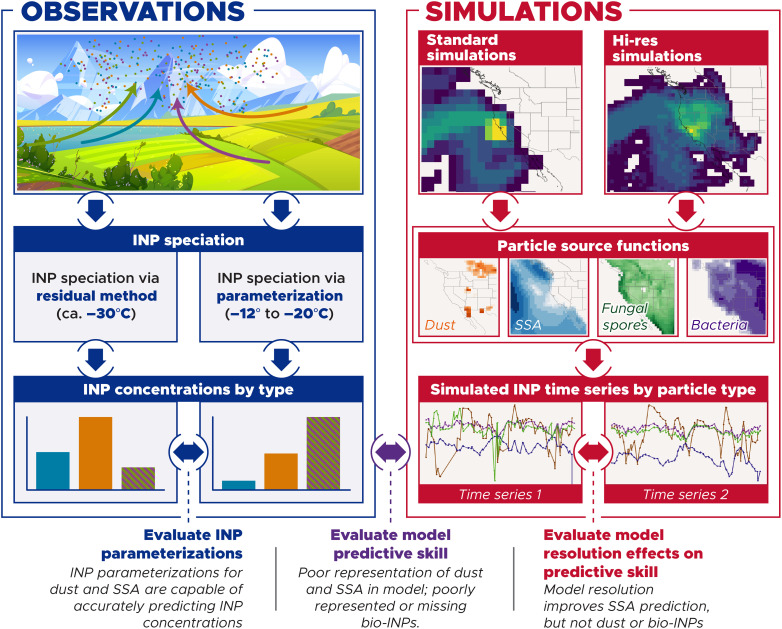
Fig. 1. Overview of the methodology used in this study.
We take two different approaches to speciate INP concentrations using single-particle techniques. The first approach uses the direct measurements of ice crystal residuals with an SPMS to fractionate INP concentrations. The second approach uses single-particle measurements in tandem with size distributions to derive speciated particle surface area distributions. We then apply particle type–specific active site density ns parameterizations to calculate INP concentrations for different particle types. These two approaches can be used to evaluate the representativeness of dust and SSA INP parameterizations. We take a Lagrangian approach to evaluate model predictive skill. We use a turbulent dispersion model, FLEXPART, to calculate source-receptor influence footprints and combine these source-receptor footprints with particle source functions for dust, SSA, fungal spores, and bacteria along with appropriate ns parameterizations to predict INP concentrations. The predictive skill of the model is evaluated using the speciated INP measurements. In addition, using high- and low-resolution meteorological data to drive the Lagrangian simulations allows us to assess how model resolution affects our prediction of INP concentrations.