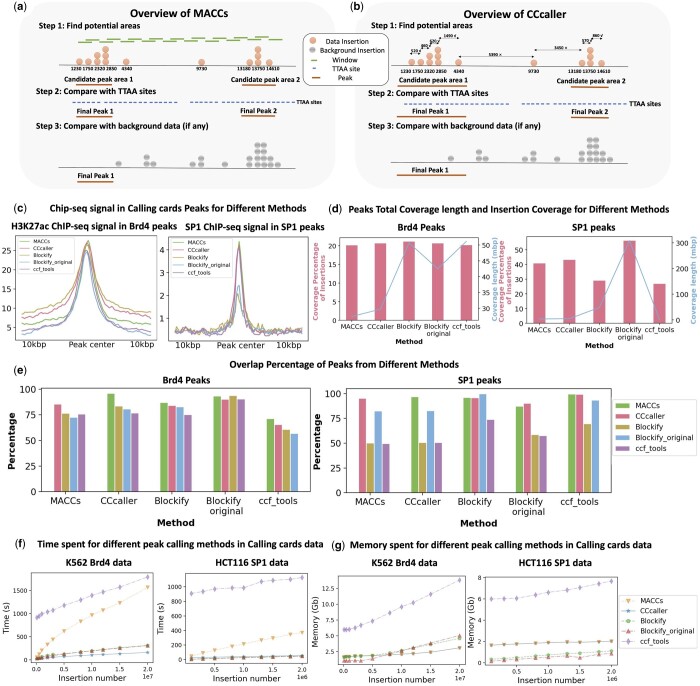
Figure 2.
Peak calling methods for Calling cards data. (a) Overview of MACCs. (b) Overview of CCcaller. (c) Chip-seq signal in calling cards peaks for the different peak calling methods in Pycallingcards (left: peaks calling without background, HCT116 Brd4 data; right peaks calling with background, HCT116 SP1 data). (d) The percentage of insertions contained under all called CC peaks is plotted for different methods (pink bars). On the same plot, the cumulative peak length of all called peaks is plotted (blue bars, left: peaks calling without background, K562 Brd4 data; right peaks calling with background, HCT116 SP1 data). (e) Percentage of peaks that overlap between the different peak calling methods. [left: K562 Brd4 data (no background peak calling); right: HCT116 SP1 data (peaks calling with background)]. (f) Computational time required for each of the different peak calling methods in Pycallingcards [left: K562 Brd4 data (no background peak calling); right: HCT116 SP1 data (peaks calling with background)]. (g) Memory required for different peak calling methods in Calling cards data (left: peaks calling without background, K562 Brd4 data; right peaks calling with background, HCT116 SP1 data).