FIGURE 4:
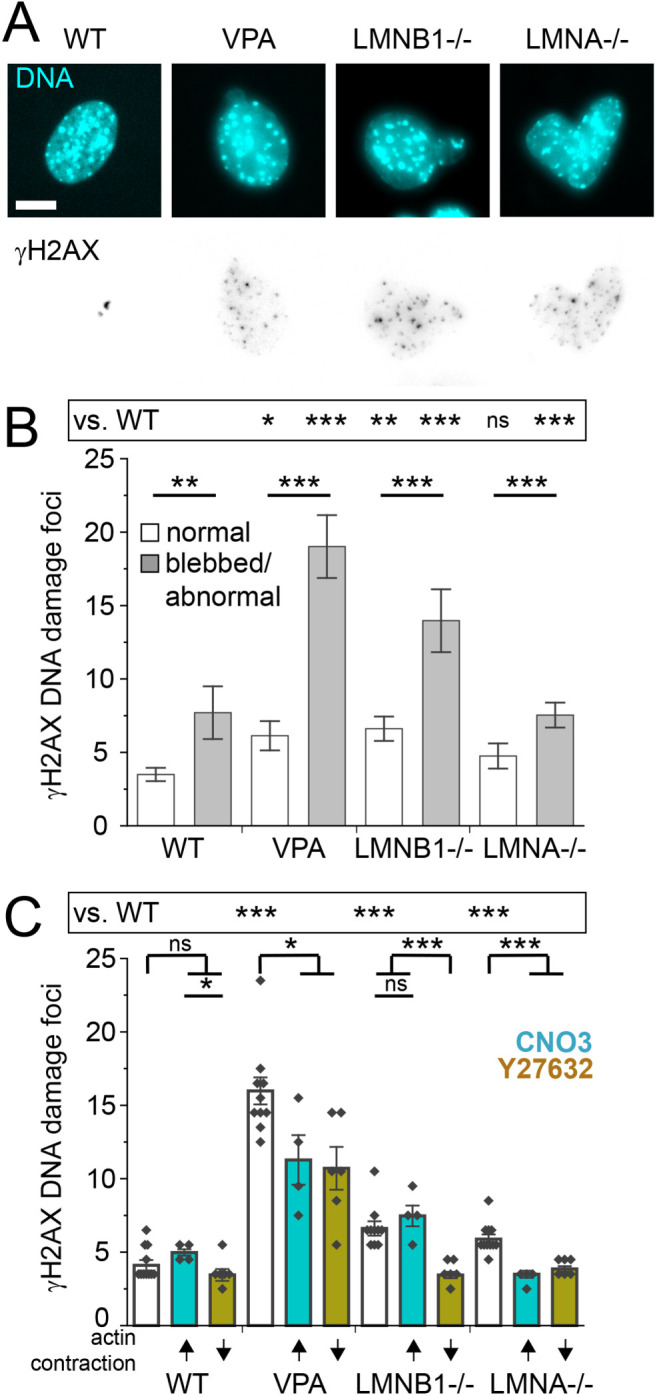
Increased DNA damage is associated with nuclear shape and can be rescued by actin contraction inhibition. (A) Representative images of nucleus shape via labeling DNA (Hoechst, Cyan) and DNA damage foci (γH2AX, inverted gray scale). (B) Graph of number of γH2AX DNA damage foci for normally shaped nuclei versus blebbed/abnormal (WT normal n = 115, blebbed n = 17; VPA normal n = 119, blebbed n = 55; LMNB1−/− normal n = 103, blebbed n = 32, LMNA–/– normal n = 73, abnormal circularity < 0.9 n = 214 [see Supplemental Table 1]). (C) Graph of number of γH2AX DNA damage foci for WT, VPA, LMNB1−/−, and LMNA−/− without modulation (white bar), with increased actin contraction (turquoise bar, CN03), or with decreased actin contraction (gold bar, Y27632). Multiple biological replicates of unmodulated (n = 10), increased (n = 4) and decreased (n = 6) actin contraction. Experiments represented by black dots, where n > 40 cells per experiment. Student’s t test p values reported as * < 0.05, ** < 0.01, *** < 0.001, or ns denotes no significance, p > 0.05. Error bars represent standard error. Scale bar = 10 µm.
