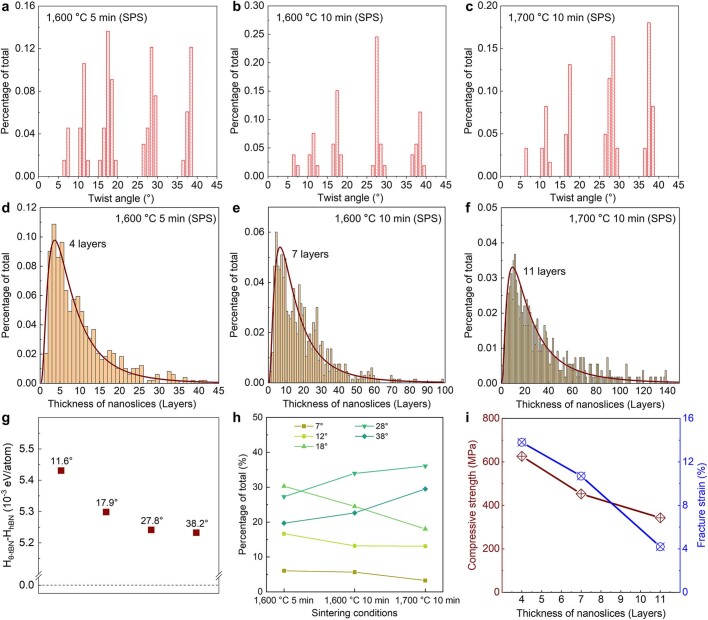
Extended Data Fig. 7. Statistical distribution of twist angles and nanoslice thickness, and the relationships between synthesis parameters, microstructure, and mechanical properties in SPS sintered TS-BN ceramics.
a-c, Distribution of twist angles in ceramics obtained at various conditions, 1,600 °C, 5 min (a); 1,600 °C, 10 min (b); and 1,700 °C, 10 min (c). The twist angles are concentrated at four main angles (~38°, ~28°, ~18°, and ~12°) and a non-dominant angle of ~7°. Supplementary Fig. 4a shows the hypothetical twist-stacked crystal structures with twist angles of 38.2°, 27.8°, 17.9°, 11.6°, and 7°, respectively. d-f, Thickness of twistedly stacked nanoslices in ceramic nanoplates, 1,600 °C, 5 min (d); 1,600 °C, 10 min (e); and 1,700 °C, 10 min (f). As the sintering temperature and time increase, the average thickness of nanoslices increases from 4 layers to 11 layers, leading to a decrease in the density of twisted interface. g, DFT calculated enthalpies of hypothetical twisted-layer BN structures with respect to hBN. h, Percentage variation of twist angles with sintering temperature and holding time. i, Relationships between thicknesses of nanoslices and the compressive strength (and fracture strain) of TS-BN ceramics.