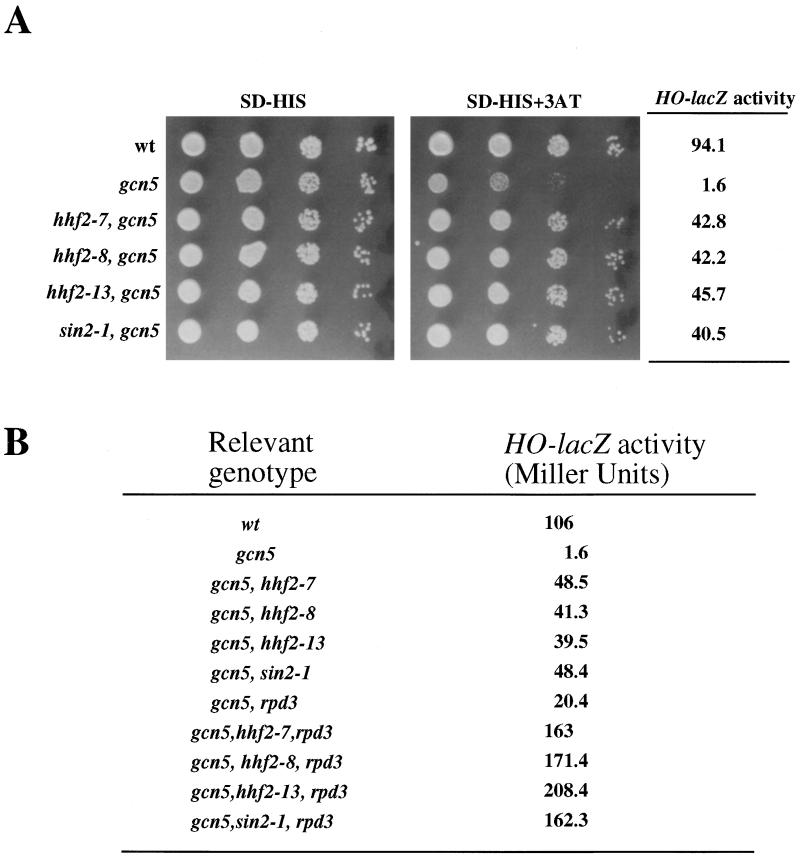
FIG. 4.
Histone sin mutations suppress gcn5 defects. (A) Cultures of JJY12 (wild type [wt]), JJY28 (gcn5::hisG), JJY41 (hhf2-7 gcn5::hisG), JJY42 (hhf2-8 gcn5::hisG), JJY43 (hhf2-13 gcn5::hisG), and JJY44 (sin2-1 gcn5::hisG) cells (approximately 5 × 106/ml) were spotted in 10-fold serial dilutions on medium lacking histidine (SD-HIS) and on medium lacking histidine and containing 10 mM 3-AT. Plates were incubated at 30°C for 3 days. The same cultures were used to measure β-galactosidase activity (in Miller units). Values are averages of three independent measurements with less than 10% deviation. (B) Effects of rpd3 deletion on the suppression of gcn5 defects by histone sin mutations and sin1 mutations. The strains used were JJY12, JJY28, and JJY41 through JJY44 (all as described for panel A), as well as JJY65 (rpd3Δ::LEU2 gcn5::hisG), JJY72 (hhf2-7 rpd3Δ::LEU2 gcn5::hisG), JJY73 (hhf2-8 rpd3Δ::LEU2 gcn5::hisG), JJY74 (hhf2-13 rpd3Δ::LEU2 gcn5::hisG), and JJY75 (sin2-1 rpd3Δ::LEU2 gcn5::hisG). Values are averages of three independent measurements with less than 10% deviation.