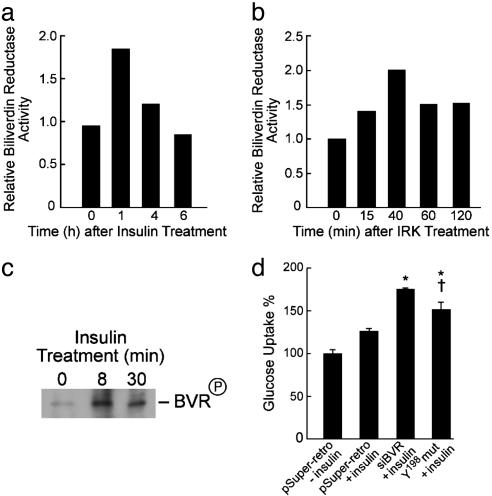
Fig. 6.
“Knock-down” BVR and Y198 deletion increase glucose uptake into 293A cells upon insulin treatments. (a) Insulin treatment increases BVR activity. 293A cells were treated with insulin (50 nM). At the indicated times, cell lysates were prepared and the reduction of biliverdin to bilirubin was measured, expressed as μmol bilirubin per min per mg, and normalized to the control. (b) BVR phosphorylation by IRK in vitro increases BVR reductase activity. Purified BVR was phosphorylated by IRK for the indicated periods. Reactions were terminated by diluting with PBS and freezing at -20°C. BVR activity was determined as in a and normalized to that of the control (43.8 μmol per min per mg). (c) Insulin treatment increases BVR tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell lysates were obtained from cells treated with insulin for 8 or 30 min and immunoprecipitated with anti-human BVR antibodies. The phosphorylated BVR was subjected to Western blot and visualized by using antityrosine antibodies and the ECL system. (d) Effect of insulin treatment on glucose uptake by cells infected with small interfering RNA for human BVR or transfected with Y198 mutant BVR. Cells were infected/transfected with the constructs shown, treated with 50 nM insulin for 15 min, and subsequently incubated in 1 ml of PBS containing 5 mM glucose and 1 μCi/ml 2-deoxy-[1-3H]glucose for 15 min. Experimental details are provided in the text. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three experiments with triplicate samples in each.