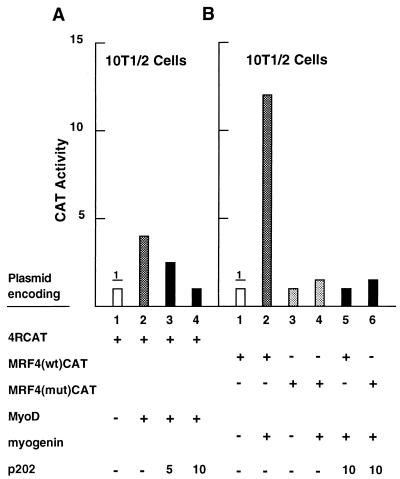
FIG. 6.
Overexpression of p202 inhibits the transcriptional activities of MyoD and of myogenin in transient-transfection assays. (A) Cultures of 10T1/2 cells were transfected with the 4RCAT reporter plasmid (2.5 μg) in which CAT expression is driven by four MyoD binding (R) sites from the muscle-specific creatine kinase gene (lanes 1 to 4), together with 10 μg of the MyoD expression plasmid (pCMV-MyoD) (lanes 2 to 4) and the p202 expression plasmid (pCMV-202) in the amounts indicated in micrograms (lanes 3 and 4). In each case, a pSVgal internal control plasmid (3.6 μg) was cotransfected and the expression vector (pCMV) was used to bring the total amount of DNA transfected to 30 μg. At 48 h after starting the transfection, the reporter activities were assayed in the cell lysates after normalization with the internal standard. Normalized CAT activity in the experiment in lane 1 was defined as 1. (B) Cultures of 10T1/2 cells were transfected with the MRF4(wt)CAT reporter plasmid (5 μg) (lanes 1, 2, and 5), in which CAT expression is driven by a 390-bp segment from the MRF4 gene, or the MRF4(mut)CAT reporter plasmid (5 μg) (lanes 3, 4, and 6), which differs from MRF4(wt)CAT by deletion of one E box and mutation of a second one. If so indicated, the myogenin expression plasmid (pEMSVscribe-myogenin) (10 μg) (lanes 2, 4, 5, and 6) and the p202 expression plasmid (pCMV-202) (10 μg) (lanes 5 and 6) were also transfected. In each case, pSVgal (internal control plasmid) (3.6 μg) was cotransfected. Salmon sperm DNA was used to bring the total amount of DNA transfected to 30 μg. At 48 h after starting the transfection, cell lysates were prepared and assayed for CAT activity as described for panel A. For further details, see Materials and Methods.