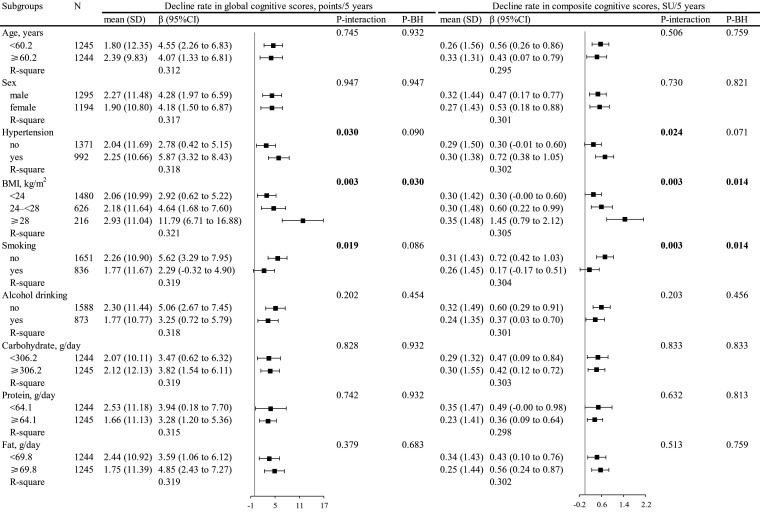
Figure 2.
Subgroup analyses for the association between dietary thiamine intake and the 5-year decline rate in cognitive scores in participants with dietary thiamine intake higher than the inflection point (0.68 mg/day). (Adjusted, if not stratified, for age, sex, global score, smoking, alcohol consumption, BMI, SBP, DBP, education level, occupation, region, urban or rural residency, self-reported diabetes, antihypertensive medication, physical activity, as well as the intakes of fibre, sodium, potassium, carbohydrate, protein and fat. Hypertension was defined as SBP≥140 mm Hg or DBP≥90 mm Hg, or diagnosed by a physician, or currently under antihypertensive treatment.) BMI, body mass index; CI, confidence interval; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; P-BH, multiple testing corrected p values by Benjamini-Hochberg method; SBP, systolic blood pressure; SD, standard deviation; SU, standard units by averaging z scores.