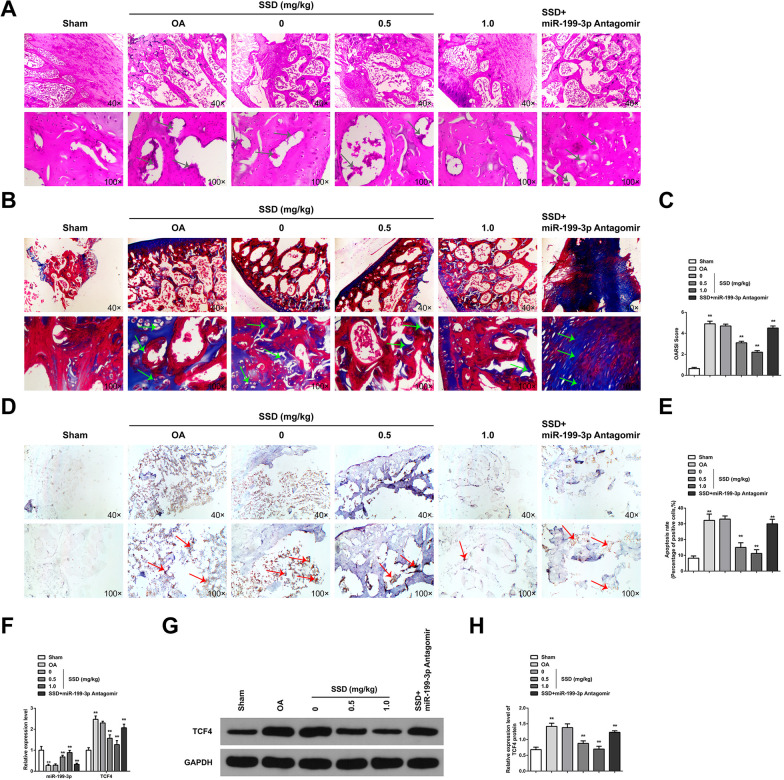
Fig. 1.
SSD relieves cartilage damage in OA mice via elevating miR-199-3p. A HE staining observed articular cartilage damage. The results showed that AC tissue in Sham group showed smooth surface and complete structure; while, OA cartilage tissue showed rough surface and cartilage destruction. SSD treatment improved cartilage damage, and downregulation of miR-199-3p weakened the protective effect of SSD on OA cartilage, arrows indicate cartilage damage; B Safranine O-fast green staining observed AC damage and showed that chondrocytes were regularly arranged in Sham group; while, the cartilage tissue degradation of OA mice was severe. SSD treatment could reduce the degradation of cartilage tissue, and downregulation of miR-199-3p weakened the protective effect of SSD on OA cartilage, arrows indicate cartilage degradation; C OARSI score evaluated the injury of AC, and the results showed that OARSI score increased in OA mice. SSD treatment could reduce OARSI score, and downregulation of miR-199-3p decreased the effect of SSD; D–E TUNEL staining tests showed that apoptosis of articular chondrocytes increased in OA mice, arrows indicate chondrocyte apoptosis. SSD treatment reduced the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes, and down-regulating miR-199-3p weakened the inhibitory effect of SSD on the apoptosis of OA chondrocytes; F RT-qPCR detected mRNA expression of miR-199-3p and TCF4. The results showed that miR-199-3p was downregulated and TCF4 mRNA was upregulated in the cartilage tissue of OA mice. SSD treatment promoted miR-199-3p expression and inhibited TCF4 mRNA, and downregulation of miR-199-3p decreased the effect of SSD; G–H Western blot detected TCF4 protein expression. TCF4 was upregulated in the cartilage tissue of OA mice. SSD treatment inhibited TCF4 protein expression, and downregulation of miR-199-3p decreased the effect of SSD. A,B,D, scale bar = 20 μm. A–D, the mice in each group. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01. n = 10