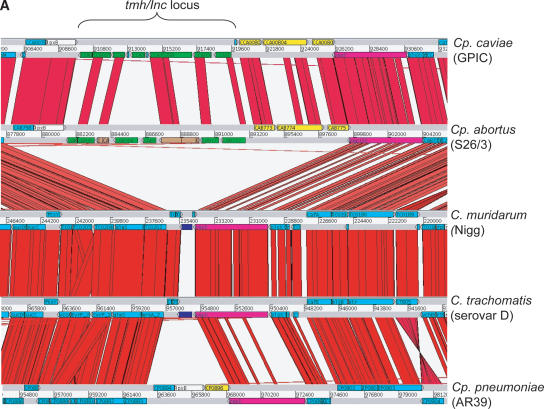
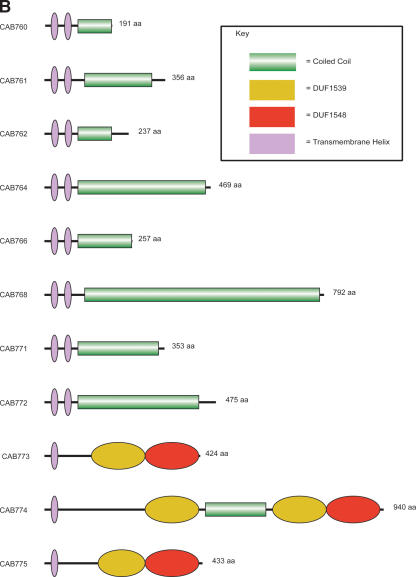
Figure 3.
(A) Comparison of the tmh locus of Cp. caviae (GPIC), Cp. abortus (S26/3), C. muridarum (Nigg), C. trachomatis (serovar D), and Cp. pneumoniae (AR39). ACT (see Fig. 2) comparison of amino acid matches between the complete six-frame translations (computed using TBLASTX) of representatives of the five sequenced Chlamydiaceae species. The red bars spanning between the genomes represent individual TBLASTX matches. CDS are marked as colored boxes positioned on the gray DNA lines: tmh family (green for intact genes, brown for pseudogenes), pmpD (pink), those carrying both DUF1539 and DUF1548 motifs (yellow), CDS encoding products with paired N-terminal TM domains (dark blue), lipid A biosynthesis (white), and all others (light blue). The scale is marked in base pairs. The region shown for Cp. pneumoniae strain AR39 is identical in all of the other sequenced Cp. pneumoniae strains (data not shown). (B) Architecture of the proteins encoded at the tmh locus of Cp. abortus. The amino acid sequences of the two pseudogenes CAB762 and CAB768 have been artificially reconstructed for the purpose of this analysis. See key for color codes. (DUF) Domain of unknown function.