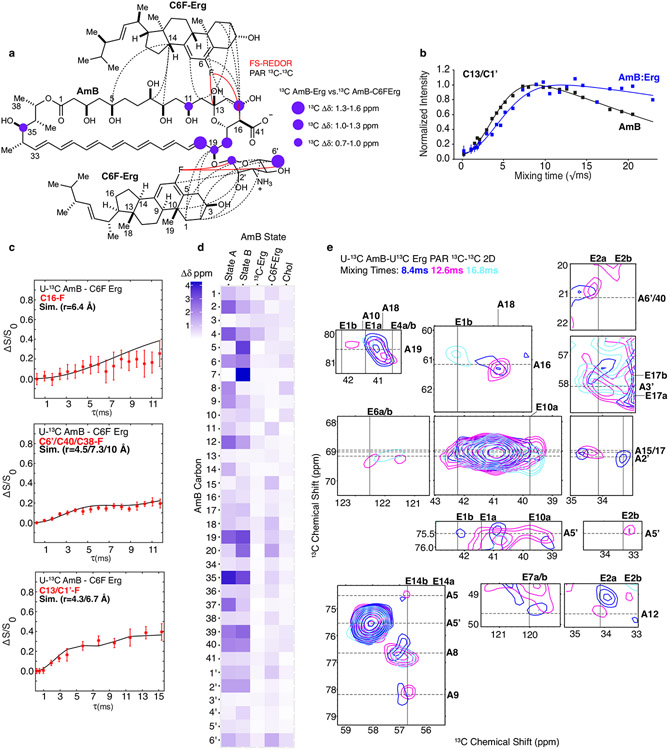
Extended Data Fig. 3 ∣. Erg interacts with AmB through contacts between the sterol rings and conserved GPM motif.
a, A diagram summarizing AmB-Erg interactions shown in c, d, and e, highlighting 13C-13C and 19F-13C interactions between the Erg A and B rings and the conserved C11-C20 motif and mycosamine. b,13C detected 1H-1H polarization transfers from water to the 13C-AmB C13/C1’ signal for homogenized 13C-AmB (black line) and 13C-AmB:Erg complexes (blue lines). Each data point comes from one peak (n = 1). Error bars represent uncertainties from the signal-to-noise ratio of each spectrum. c, Dephasing curves (red stars for experimental data and black lines for simulated curves) from 13C{19F} frequency selective REDOR experiments performed on a 13C-AmB:C6F-Erg sample and corresponding distances calculated from the dipolar couplings. Data presented as mean +/− SD of n = 11, 5, and 10 technical replicates, respectively. Error bars indicate uncertainty from the spectrum signal-to-noise ratio. d, AmB chemical shift perturbations relative to Erg bound 13C-AmB for the apo AmB states, previously reported in Nat. Chem. Bio. 28, 972 (2021), and 13C-AmB bound to 13C-Erg, C6F-Erg, and Chol (SI Table 6). e, Overlay of 13C-13C 2D PAR spectra collected at 8.4 ms (blue), 12.6 ms (magenta), and 16.8 ms (cyan) mixing times obtained from a 13C-AmB:13C-Erg sample highlighting interactions between the two primary Erg ring states and AmB.