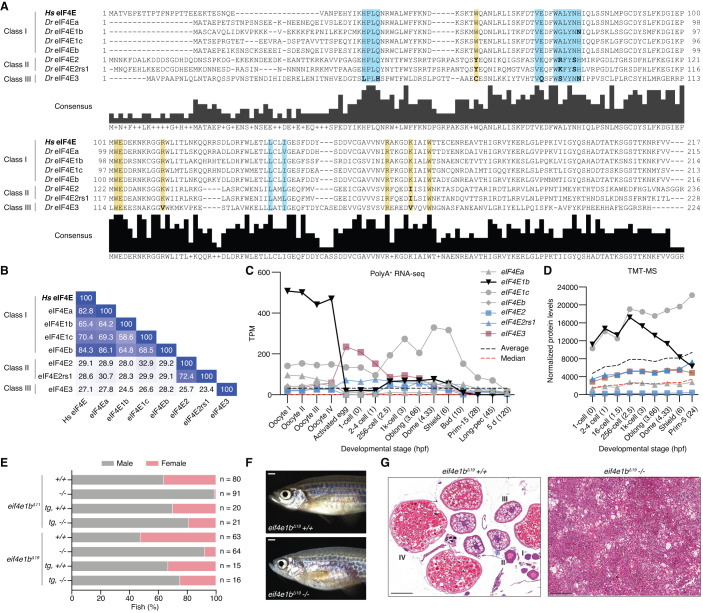
Figure 1. eIF4E1b is a class I eIF4E protein with an essential role in zebrafish oogenesis.
(A) Alignment of human (Homo sapiens, Hs) and zebrafish (Danio rerio, Dr) eIF4E proteins. Highlighted regions indicate the amino acids involved in the interaction with the mRNA cap (yellow) and eIF4E-binding motifs (blue); residues in the highlighted regions with a different polarity than human eIF4E are indicated in bold. (B) Percentage identity matrix of the proteins shown in (A). (C) The abundance of eIF4E transcripts during zebrafish oogenesis and embryogenesis based on published polyA-selected RNA-seq data (Pauli et al, 2012; Cabrera-Quio et al, 2021). TPM transcripts per million. X axis indicates developmental stages (hours post fertilization, hpf, in brackets). (D) eIF4E protein levels (represented with the same colors and symbols as in (C) during early zebrafish embryogenesis obtained by tandem mass tag mass spectrometry (TMT-MS), normalized to spike-in proteins. X axis indicates developmental stages (hpf in brackets). (E) Percentage of males and females of homozygous (−/−) and wild-type (+/+) siblings obtained from heterozygous eif4e1b incrosses (n = number of fish), as determined by secondary sexual characteristics. Expression of 3xflag-sfGFP-eIF4E1b (tg) partially rescues the male bias observed in the two homozygous fish mutants. (F) Representative images of wild-type (top) and homozygous eif4e1b (bottom) female siblings (scale bar = 1 mm). (G) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of sectioned ovaries isolated from wild-type and homozygous eif4e1b fish. Mutant ovaries have no oocytes. Stages of oocyte development are indicated with roman numbers in the wild-type ovary sections. Scale bars = 200 μm. Source data are available online for this figure.