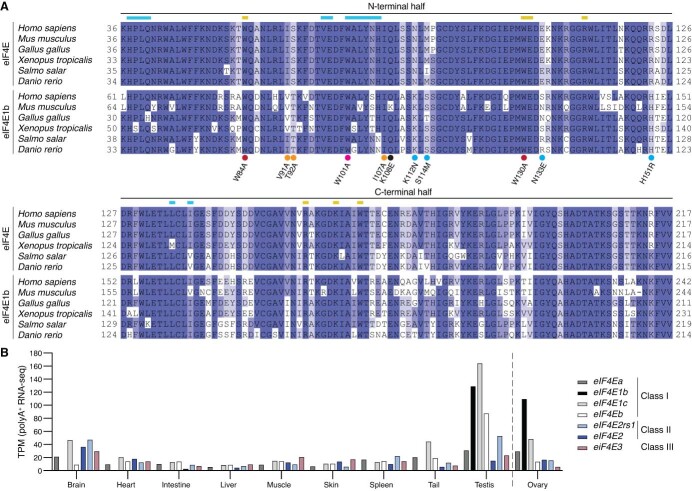
Figure EV1. eIF4E1b and eIF4E are highly conserved but have specific expression patterns.
(A) Amino acid alignment of eIF4E and eIF4E1b proteins from six vertebrate species. Unstructured N-terminal regions (see Fig. 1A), which are not included in the constructs used for expressing recombinant proteins, are excluded from the alignment. Residues interacting with the mRNA cap or with eIF4E-binding motifs are highlighted with yellow or blue lines, respectively. eIF4E1B residues mutated in Fig. 3D are indicated with dots (red: mRNA cap binding; pink: dorsal site; orange: lateral site; blue: conserved in eIF4E but different in eIF4E1b proteins; black: others). N-terminal and C-terminal regions exchanged in chimeric constructs are indicated. (B) mRNA levels (in transcripts per million, TPM) of zebrafish eIF4Es in different organs and adult tissues based on polyadenine-selected RNA-seq data (Fujihara et al, 2021) (ovary RNA-seq data from Herberg et al, 2018).