Figure 1. m7G-tRNA modification prevents ribosome stalling at m7G-tRNA decoded codons.
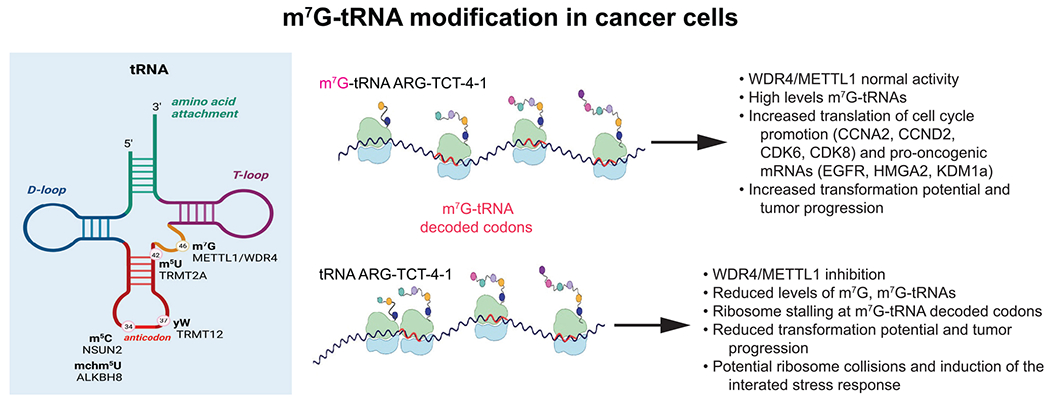
Shown is an overview of tRNA modifications associated with increased oncogenic activity, including m7G modification of nucleotide position 46. The METTL1/WDR4 enzymatic complex carries out m7G modification of a subset of tRNAs that decode m7G-tRNA-dependent codons, thereby promoting normal ribosome elongation without stalling. Certain cell cycle and pro-oncogenic mRNAs that are enriched in m7G-tRNA-dependent codons are increased in their translation, thereby increasing oncogenic potential. Reduction in METTL1/WDR4 activity results in ribosome stalling, shown specifically for the m7G-modified ARG-TCT-4-1 tRNA, resulting in reduced translation of these same mRNAs, resulting in reduction in transformation and cancer progression.
