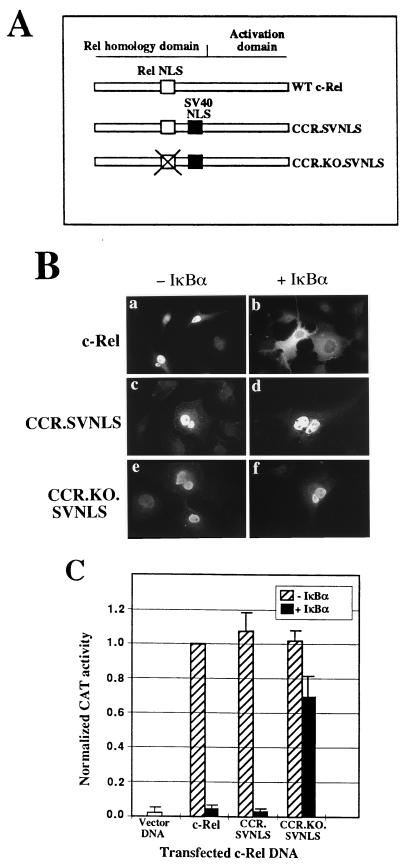
FIG. 1.
c-Rel mutants that bypass cytoplasmic regulation by IκBα. (A) Structures of the CCR.SVNLS and CCR.KO.SVNLS mutants of c-Rel. The Rel NLS and the SV40 NLS are depicted as white and black boxes, respectively. Mutation of the Rel NLS in CCR.KO.SVNLS is indicated by X. WT, wild type. (B) Subcellular localization of c-Rel and c-Rel-derived mutants. Cos-7 cells cotransfected with wild-type or mutant c-rel genes, together with CMV or CMV iκbα expression plasmids, were analyzed by indirect immunofluorescence with an anti–c-Rel antibody. (C) Transcriptional activity of wild-type and mutant c-Rel proteins. Cos-7 cells were transfected with CMV vector DNA or with expression plasmids encoding c-Rel or c-Rel-derived mutants, alone or together with an expression vector for IκBα. The pIL6CAT reporter plasmid, containing three κB DNA sites upstream of the interleukin-6 promoter, was included in the transfection. The average CAT activity from three independent experiments was normalized to that of wild-type c-Rel.