Figure 1.
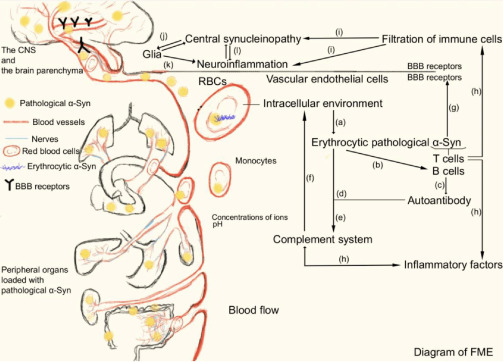
Diagram of FME and the propagation mode of pathological α-Syn from peripheral organs to the brain.
The FME is composed of pathological α-Syn, the peripheral immune system, members of the BBB, the erythrocytic intracellular environment, and soluble and insoluble cytokines. (a) The erythrocytic intracellular environment contributes to the generation of pathological α-Syn. (b) Erythrocytic pathological α-Syn recruits B cells. (c) B cells secrete autoantibodies against α-Syn. (d) Autoantibodies of α-Syn promote clearance of erythrocytic pathological α-Syn. (e) A combination of α-Syn and its antibody leads to activation of the complement system. (f) Members of the complement system reversely aggravate α-Syn pathology. (g) T cells discriminate peptides of α-Syn and perform antigen presentation. (h) Recruiting of B and T cells and vesicle trafficking of pathological α-Syn give rise to infiltration of inflammatory factors and peripheral pathological α-Syn across the BBB. (i–l) Penetration of peripheral immune cells and peripheral pathological α-Syn causes central synucleinopathy and neuroinflammation. Created with Adobe Illustrator. BBB: Blood-brain barrier; CNS: central nervous system; FME: fibrillization microenvironment; RBC: red blood cell; α-Syn: α-synuclein.
