Table 3. A comparison of the meme, hmmer, and AF methods for motif building.
| Action | meme | hmmbuild | AF method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | An unaligned set of sequences. Motif region (if any) in each sequence may be unknown. | An aligned set of sequences. Nonhomologous sites may be removed prior to model building. | An aligned set of sequences. Entropy is used to differentiate con served from nonconserved sites. |
| Output | A set of PSSMs, one for each motif found by the algorithm. | Markov transition matrix specific to hmmer model. | A motif pattern that is mathematically very similar to a thresholded pssm. |
| Interpretability of the output | Not readily interpretable unless entries are thresholded or compared statistically. | Relatively uninterpretable. hmm is a nonconstructive statistical null hypothesis. | A readily interpretable motif pattern. |
| Strengths and weaknesses | Does not need an initial alignment to find or create motifs. | Requires initial sequence alignment. | Requires an initial sequence alignment. |
| Search algorithm gives an estimate of how well the motif fits a test sequence. | Picking conserved regions to train model is subjective. | A priori biological knowledge can be included. | |
| Search algorithm gives an estimate of how well the motif fits a test sequence. | Mismatch count is correlated with probability of motif family membership. |
PSSM, position-specific scoring matrix; thresholding refers to mapping 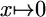 if x < ε and
if x < ε and 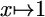 otherwise.
otherwise.
