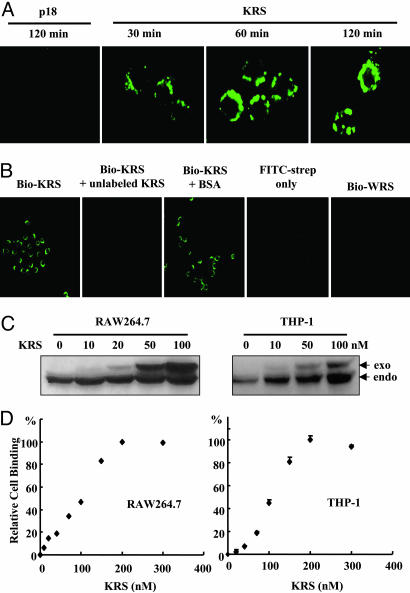
Fig. 2.
Specific binding of KRS to immune cells. (A) KRS or p18 was biotinylated and incubated with RAW264.7 cells, which were harvested at the indicated times. The cell-bound KRS was reacted with FITC-conjugated streptavidin and visualized by confocal immunofluorescence microscopy. (B) The cell binding specificity of KRS. RAW264.7 cells were pretreated with unlabeled KRS or BSA, and the biotinylated KRS was added subsequently. The biotinylated WRS was also incubated with RAW246.7 cells. (C) RAW264.7 and THP-1 cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of the His-tagged KRS, and, after they were harvested, the proteins were extracted. The exogenously added (exo) and endogenous (endo) KRS were detected by Western blotting with an anti-KRS antibody. (D) Cell binding by KRS was monitored as above and quantified with a phosphoimage analyzer (Fuji), and the amount of the cell-bound KRS was plotted.