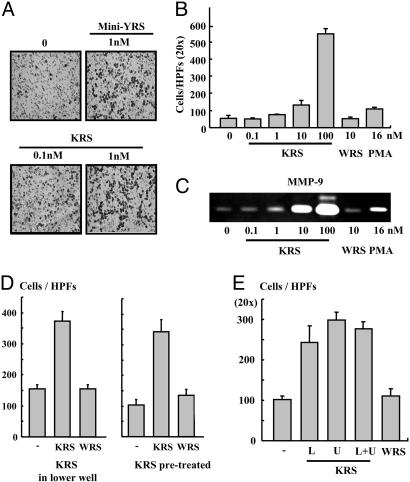
Fig. 4.
The effect of KRS on cell migration. (A) RAW264.7 cells (3 × 105) and KRS (10 nM) were added to the upper and lower wells of Transwell chamber, respectively, and the cells migrated through the membrane were detected by the hematoxylin staining as described in Materials and Methods. (B) Dose-dependent cell migration by KRS. (C) The KRS-dependent induction of MMP-9 was determined by a zymographic assay. RAW264.7 cells, treated as above, were lysed, and the proteins were resolved on SDS/PAGE-containing gelatin. The hydrolysis of gelatin was determined as described in ref. 28. (D Left) To determine how KRS induces cell migration, RAW264.7 cells were loaded onto the upper well, and KRS or WRS was added to the lower well and allowed them to migrate. (Right) The cells were pretreated with 10 nM KRS or WRS for 30 min and loaded to the upper well and incubated them to migrate without adding KRS or WRS to the lower well. Then, the migrated cells through the membrane were counted as above. (E) The cell migration was also determined in the Transwell chambers in which 10 nM KRS was added to the upper or lower or both wells. As the control, no KRS was added, or 10 nM WRS was added to the lower well.