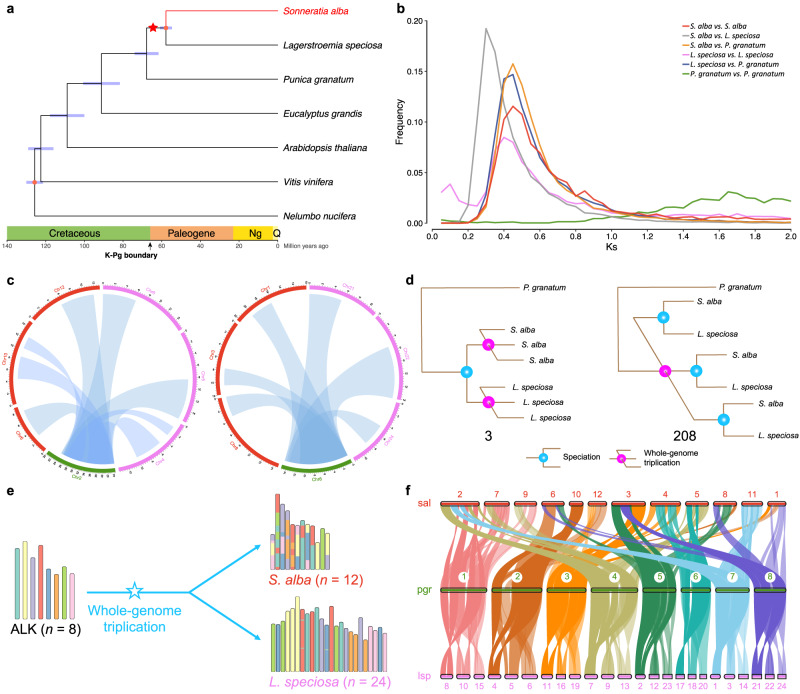
Fig. 2. The whole-genome triplication (WGT) event is shared in S. alba and L. speciosa.
a Phylogenetic tree of seven eudicots, including S. alba and relatives. Blue node bars are 95% confidence intervals. Red nodes indicate two fossil calibration nodes. The star represents the WGT event. The occurrences of the K-Pg boundary and PETM are indicated by the arrows on the timeline. b Ks distribution between paralogous genes within the same species and orthologous genes from pairs of species. c Synteny between the homologous regions of S. alba (red), L. speciosa (pink), and P. granatum (green). It reflects the overall synteny relationship with a 3:1 ratio between S. alba vs. P. granatum, L. speciosa vs. P. granatum, respectively. The representation showcases partial regions of the genomes. d Numbers of homologous gene groups supporting different scenarios on the order of speciation and WGT events in Sonneratia and Lagerstroemia. e Chromosome evolution following WGT from the ALK (the ancestral Lythraceae karyotype). The star represents the WGT event. f Macrosynteny patterns among the three Lythraceae plants. “sal” represents S. alba, “pgr” represents P. granatum, and “lsp” represents L. speciosa.