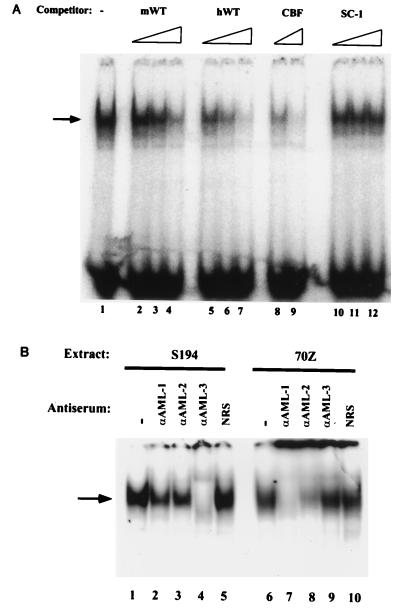
FIG. 8.
The murine and human μ enhancers bind CBF in B-cell nuclear extracts. (A) In vitro competition assays with CBF bound to a high-affinity consensus binding probe. EMSAs were carried out with 20 μg of S194 nuclear extracts with 32P-labeled CBF oligonucleotide DNA probes (50,000 cpm), in the presence of no competitor DNA (lane 1), 5-, 25-, and 133-fold molar excesses of murine μ enhancer DNA (lanes 2 to 4) and human μ enhancer DNA (lanes 5 to 7), and 8- and 33-fold molar excesses of self (lanes 8 and 9) and 16-, 32-, and 66-fold molar excesses of nonspecific (lanes 10 to 12) competitor oligonucleotides, indicated by triangles. Specific nucleoprotein complexes are indicated by an arrow. The nonspecific competitor is a high-affinity binding site for Ets-1 (28). (B) Supershift EMSAs were carried out with 20 μg of S194 plasma cell and 27 μg of 70Z pre-B-cell extracts and a CBF high-affinity consensus binding site probe. Lanes 1 to 5 show complexes formed by the incubation of S194 extracts with CBF probes followed by no antiserum (lane 1), antiserum specific for AML-1, -2, and -3 (lanes 2, 3, and 4, respectively), and normal rabbit serum (NRS) (lane 5). Lanes 6 to 10 show complexes formed by the incubation of 70Z extracts with CBF probes followed by no antiserum (lane 6), antiserum specific for AML-1, -2, and -3 (lanes 7, 8, and 9, respectively), and normal rabbit serum (lane 10). Specific complexes are indicated by an arrow on the left.