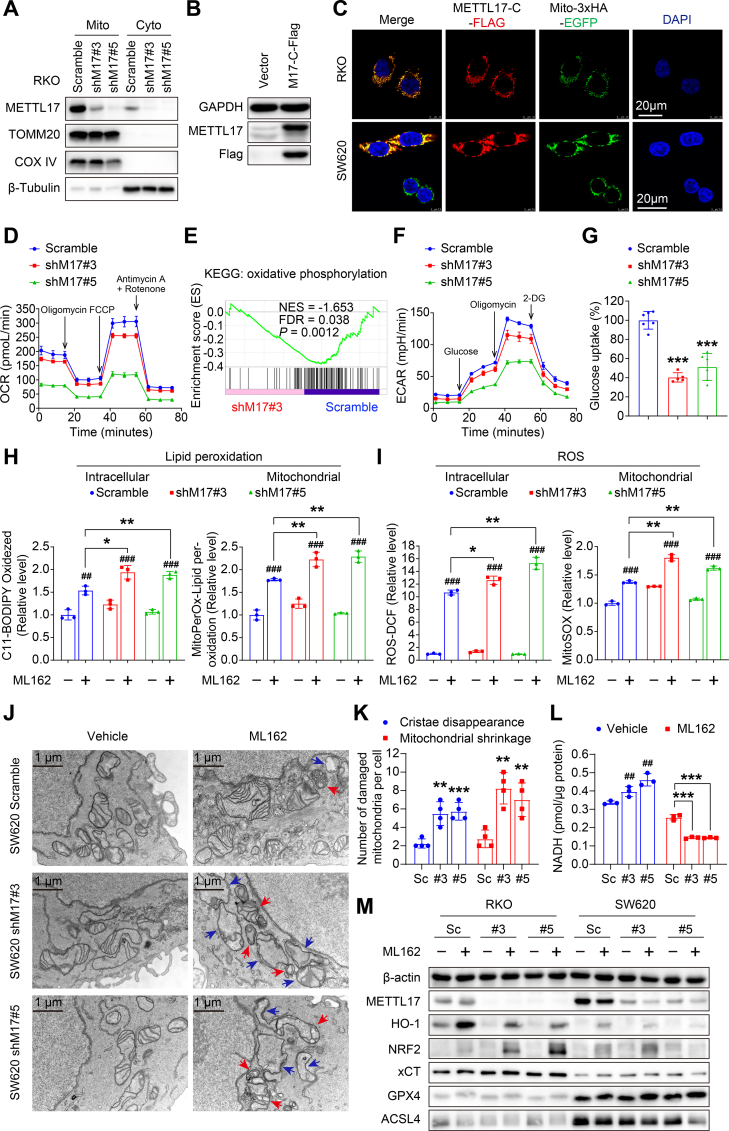
Fig. 4.
METTL17 loss causes significant mitochondrial dysfunction and promotes mitochondrial lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis.
A. Western blot analysis revealed a higher expression of METTL17 in the mitochondrial fraction compared to the cytoplasm in RKO cells. Mito, mitochondria. Cyto, cytoplasm.
B. Lentivirus mediated-overexpression of METTL17-C-Flag (M17-C-Flag) in RKO WT cells was confirmed by Western blot analysis.
C. Immunofluorescence revealed co-localization between overexpressed METTL17 and mitochondria in RKO and SW620 cells, where mitochondria were stably tagged with 3xHA-EGFP (Scale bar = 20 μm).
D. Seahorse analysis showed that METTL17 knockdown reduced oxygen consumption rate (OCR) in SW620 cells. n = 5–6 per group.
E. GSEA analysis exhibited poor oxidative phosphorylation in METTL17 loss SW620 cells. The representative down-regulated genes were presented in Supplementary Fig. 13A.
F. Seahorse analysis showed that METTL17 knockdown reduced extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) in SW620 cells. n = 5–6 per group.
G. Knockdown of METTL17 significantly suppressed the glucose uptake ability of RKO cells. n = 5–6 per group.
H and I. Knockdown of METTL17 increased intracellular and mitochondrial lipid peroxidation (H) and ROS (I) in ML162 (10 μM, 3 h)-treated SW620 cells, which were stained by indicated fluorescent dyes followed by flow cytometry detection. Relative levels were respectively quantified. n = 3 per group.
J and K. Knockdown of METTL17 caused worse mitochondrial damage in ML162 (10 μM, 3 h)-treated SW620 cells detected by transmission electron microscope. Representative images were shown (Scale bar = 1 μm), with red arrows indicating mitochondrial shrinkage and blue arrows indicating the disappearance of mitochondrial cristae (J). The number of damaged mitochondria per cell was counted in ML162-treated SW620 cells (K), n = 4 per group.
L. Knockdown of METTL17 in SW620 cells dramatically decreased cellular NADH content compared to Scramble cells after ML162 treatment (10 μM, 4 h), while METTL17 knockdown alone increased the level of NADH. n = 3 per group.
M. Western blot analysis revealed alterations in ferroptosis markers mediated by METTL17 knockdown under ML162 (10 μM, 4 h) challenge in RKO and SW620 cells. The relative protein levels were performed semi-quantitative analysis, showing as a heatmap in Supplementary Fig. 6C.
Data are shown as mean ± SD. ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 compared to Scramble group, and *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to Scramble group or the indicated two groups, based on two-sided Student's t-test.