Fig. 6.
Targeting METTL17 interacting proteins sensitizes cancer cells to ferroptosis.
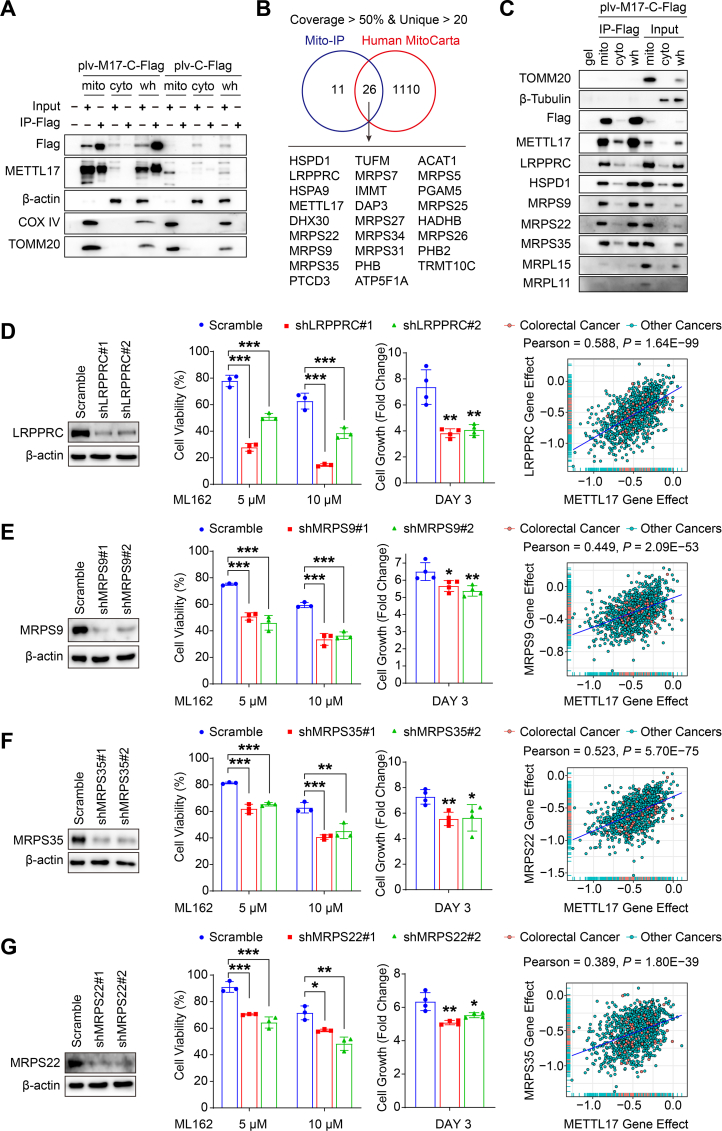
A. RKO cells overexpressing METTL17-C-Flag through plv lentivirus (plv-M17-C-Flag) were isolated into mitochondrial (mito), cytoplasmic (cyto), and whole cell (wh) fractions. Immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag affinity gel (IP-Flag) was performed, and the samples were subsequently identified by Western blot.
B. Mitochondrial precipitants (Mito-IP) were subjected to mass spectrometry analysis to identify the protein complexes binding to METTL17-C-Flag. Venn diagram analysis, based on mapping Mito-IP with Human MitoCarta, identified 26 METTL17 interactors with high affinity to METTL17, filtered by coverage >50% and unique peptide >20.
C. RKO cells overexpressing METTL17-C-Flag (plv-M17-C-Flag) were isolated into mitochondrial (mito), cytoplasmic (cyto), and whole cell (wh) fractions, and immunoprecipitated by anti-Flag affinity gel (IP-Flag). Western blot analysis of METTL17 precipitants revealed strong interactions between METTL17 and LRPPRC, HSPD1, MRPS9, MRPS22, and MRPS35.
D, E, F and H. Knockdown of METTL17-interacting proteins, LRPPRC (D), MRPS9 (E), MRPS35 (F), and MRPS22 (G) using lentivirus pLKO-shRNA, sensitized RKO cells to ML162-induced ferroptosis (n = 3 per group). Moreover, their knockdown inhibited cell proliferation in RKO cells (n = 4 per group), and the gene effect of METTL17 highly correlated with those of LRPPRC, MRPS9, MRPS35 and MRPS22. Data on gene knockout effect on cancer cells were mined from the DepMap database, with each plot representing a certain cancer cell line.
Data are shown as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 ***p < 0.001, based on two-sided Student's t-test or Pearson r-test.