Figure 10.
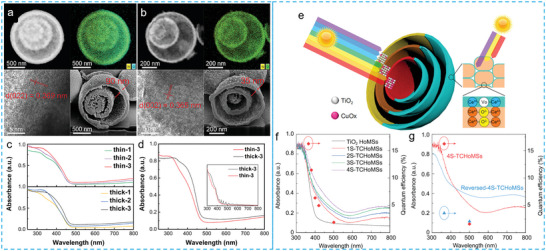
a) High‐resolution TEM (HRTEM), elemental mapping, and cross‐sectional view of thick‐3 and b) thin‐3 WO3 HoMS, respectively. c) UV–vis absorption spectra of thin and thick‐shelled samples. d) Comparison of the light‐harvesting ability between thin‐3 and thick‐3 WO3 HoMS, and inset is the calculated absorption results obtained through the finite element method.[ 78 ] Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2021, Royal Society of Chemistry. e) Illustration of two designed heterogeneous HoMS for efficient sequential harvesting of solar light. f) UV–vis absorption curves of TCHoMS with different shell numbers and apparent quantum efficiency (red diamonds) of 4S‐TCHoMS at different wavelengths. g) UV–vis absorption curves of 4S‐TCHoMS, TiO2‐CuxO nanoparticles, crushed 4S‐TCHoMS and TiO2 HoMS.[ 96 ] Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2020, Oxford University Press.
