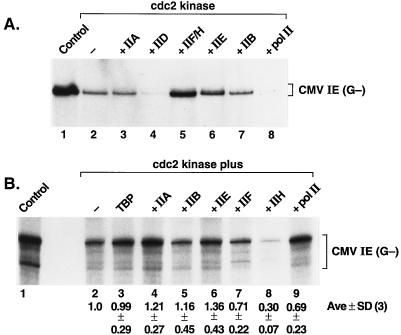
FIG. 3.
cdc2/cyclin B kinase-mediated repression of basal transcription of the CMV MIEP. (A) The TFIIF-TFIIH fraction rescues kinase-mediated repression of CMV transcription. Reactions contained a mixture of transcription factors TFIIA, TFIIB, TFIID, TFIIE, TFIIF, TFIIH, pol II, unlabeled NTPs, and [α-32P]CTP, as described in Materials and Methods, and (where indicated) 1 μl of the affinity-purified cdc2/GST-cyclin B kinase was added, followed by a 30-min incubation at ambient temperature, prior to the addition of the template DNA. Transcription factors or polymerase was added back to separate reactions as indicated above lanes 3 to 8. (B) cdc2 kinase inactivation of TFIIH. Each of the indicated factors was treated with 2 μl of cdc2/GST-cyclin B kinase and 0.2 mM ATP for 30 min at ambient temperature, and each of the nonphosphorylated factors or pol II was added back individually to separate reactions (except for the individual phosphorylated factor or polymerase in each reaction). Transcription with the CMV MIEP guanineless (G−) template was performed as described in Materials and Methods. Below each lane is shown the relative level of transcription (average value from three individual experiments ± standard deviation [SD]) as determined by phosphorimage analysis of the dried gel. Lanes 1, control reaction without added kinase; lanes 2, reaction products obtained when no protein was added back after the cdc2 kinase treatment.