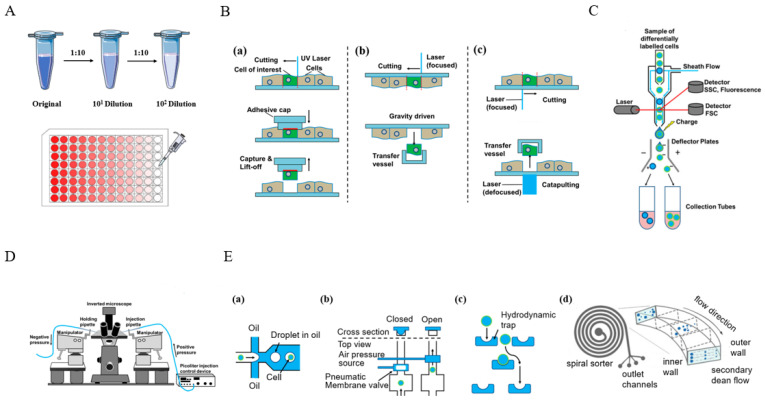
Figure 2.
The five most-used single-cell isolation methods. (A) Schematic overview of limited serial dilution. (B) Schematic overview of laser capture microdissection (LCM) methods. (a) Contact-based via adhesive tapes. (b) Cutting with a focused laser followed by capture with a vessel. (c) Cutting with a focused laser followed by pressure catapulting with a defocused laser pulse. (C) Schematic overview of fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). (D) Schematic overview of micromanipulator. (E) Schematic overview of different microfluidic methods for single-cell isolation. (a) Droplet-in-oil-based isolation. (b) Pneumatic membrane valving- based isolation. (c) Hydrodynamic cell traps-based isolation. (d) Dean flow-based isolation. Reprinted from ref. [13].