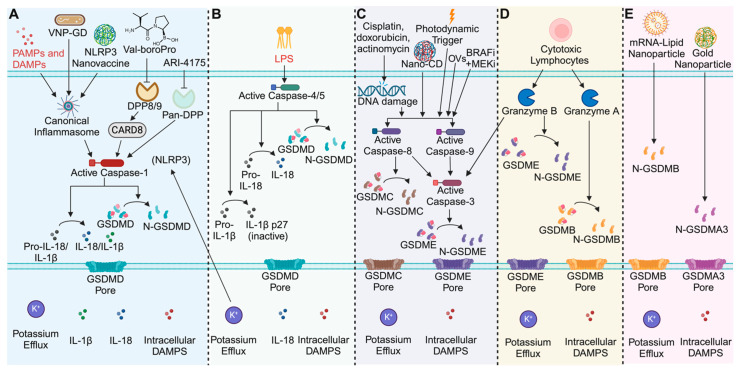
Figure 1.
Overview of pyroptosis mechanisms and pyroptosis-based therapeutics. (A) Schematic of the canonical inflammasome pathway. Inflammasome oligomerization activates caspase-1, which cleaves and activates IL-1β, IL-18, and GSDMD. Therapeutic strategies like the synthesized glutathione (GSH)-responsive GSDMD protein cages tethered to an attenuated Salmonella typhimurium (VNP) strain (VNP-GD), the NLRP3 activating nanovaccine, and the DPP inhibitors Val-boroPro and ARI-4175 activate caspase-1 to treat cancer. (B) Schematic of the human non-canonical inflammasome pathway. Caspases-4/5 detect intracellular LPS and convert IL-18 and GSDMD to their active forms, while deactivating IL-1β. (C) Schematic of the apoptotic pathways that induce gasdermin-mediated cell death. DNA damage by chemotherapeutics, targeted small molecules, photodynamic triggers, oncolytic viruses (OVs) and the nanoparticle approach (NanoCD) induce apoptotic caspase activation. Caspases-3, and -8, cleave GSDME or GSDMC respectively to induce apoptosis. Caspases-8/9 can also activate caspase-3 to execute GSDME-mediated pyroptosis. (D) Cytotoxic lymphocytes inject granzymes into target cells. Granzyme B cleave GSDME and Granzyme A cleaves GSDMB to induce pyroptosis. (E) Next-generation nanoparticle approaches deliver activated gasdermin proteins to directly induce pyroptosis. Image created with Biorender.