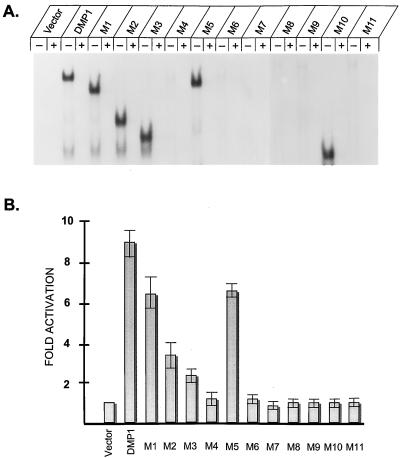
FIG. 2.
Identification of DNA binding and transactivation domains of DMP1. (A) EMSAs performed with DMP1 proteins produced in NIH 3T3 cells and with a radiolabeled DMP1-specific (BS2) probe containing the consensus binding sequence CCCGTATGT. NIH 3T3 cells were transfected with expression vectors encoding the indicated wild-type or mutant DMP1 proteins, and nuclear lysates were used for EMSA. Binding assays were performed in the absence (−) or presence (+) of excess competing oligonucleotide. (B) Results of transactivation assays performed in serum-starved NIH 3T3 cells using expression vectors encoding a DMP1-responsive luciferase reporter gene together with vectors specifying wild-type or mutant DMP1 proteins. Luciferase assays were performed 60 h after transfection, and cells were starved for serum for 18 h before assay. Error bars indicate standard deviations from the mean from multiple experiments.