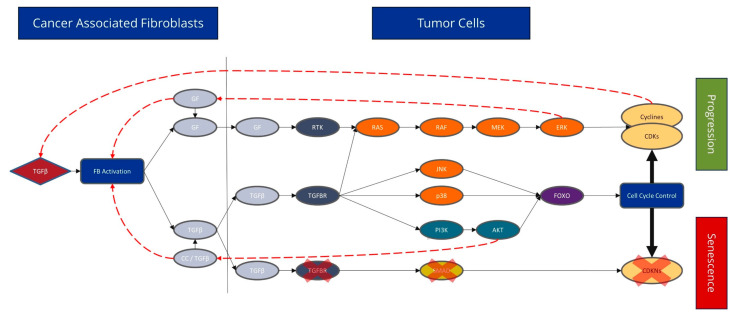
Figure 3.
The expression of different signalling pathways involved in TGF-β (Black solid arrows). Tumour cells produce TGF-β, which acts on the fibroblasts via the TGFB1 receptor, and the actual canonical pathway is completely switched off in fibroblasts. TGF-β is responsible for apoptosis and G1 arrest of cells; fibroblasts become persistent after switching the pathway off (marked by the red X). TGF-β expression may also lead to non-canonical TGF-β signal transduction via the p38 MAPK. As a result, fibroblasts secrete various growth factors, which trigger mitogenic signalling in the tumour (red dashed arrow). Subsequently, cell cycle activation causes cells to move from the G1 phase directly to the S phase. Apoptosis and cell cycle arrest are particularly affected by CAFs.