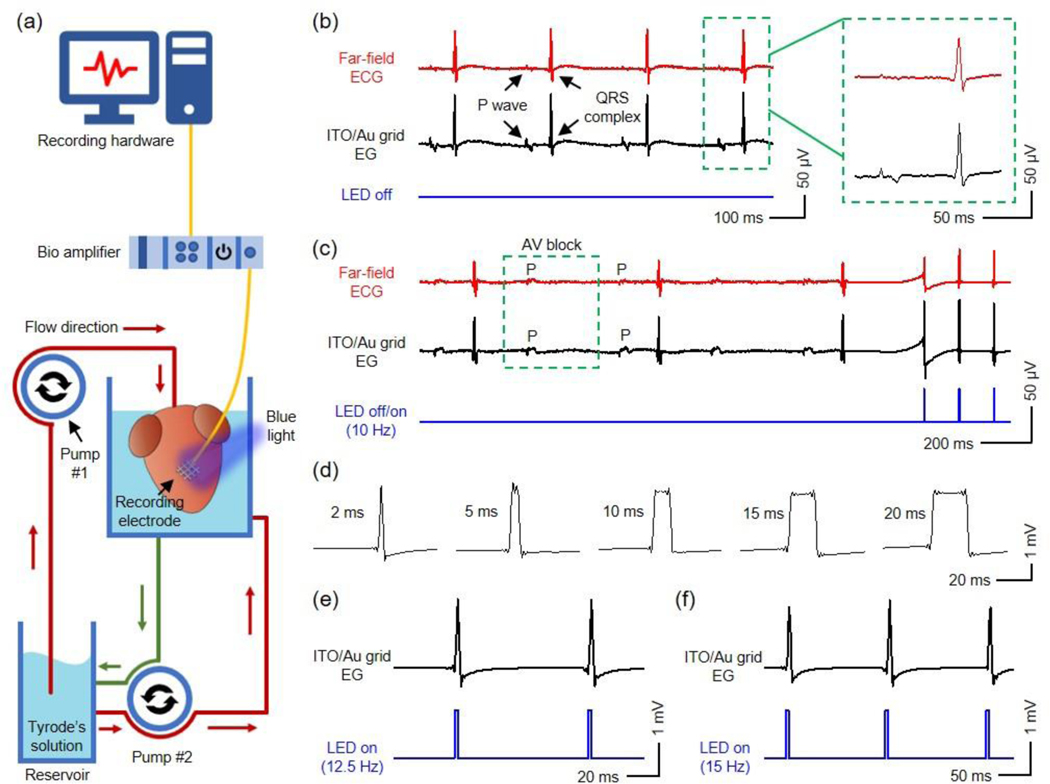
Figure 5.
(a) Schematic illustration of the Langendorff-perfusion setup used for electrophysiological recording and optogenetic pacing of ChR2-expressing mouse hearts in this work. The heart is perfused with Tyrode’s solution in a custom-designed chamber at 37 °C. Pump #1 perfuses the heart, and Pump #2 circulates solution throughout the chamber. An ITO/Au grid hybrid microelectrode is laminated onto the right ventricle of the heart and connected to a bio amplifier that interfaces with a computer where signals are recorded. (b) (Left) Far-field ECG and electrogram recordings of normal sinus rhythm from a reference electrode and an ITO/Au grid hybrid microelectrode with the blue LED turned off, respectively. (Right) Representative P waves and QRS complexes recorded by the reference electrode and ITO/Au grid hybrid microelectrode. (c) Electrogram recording from the ITO/Au grid hybrid microelectrode during 2nd degree AV block with and without simultaneous optogenetic pacing with a blue LED pulsing at 10 Hz (lower blue curve). The electrogram signals during optogenetic pacing are divided by 20 to present similar scale to that of the signals acquired during intrinsic rhythms. (d) Representative QRS complexes recorded by the ITO/Au grid hybrid microelectrode in response to blue LED stimulation at 2, 5, 10, 15, 20 ms, respectively. Representative electrogram recordings of heart rhythm from the ITO/Au grid hybrid microelectrode with the blue LED pulsing at (e) 12.5 Hz and (f) 15 Hz, respectively.