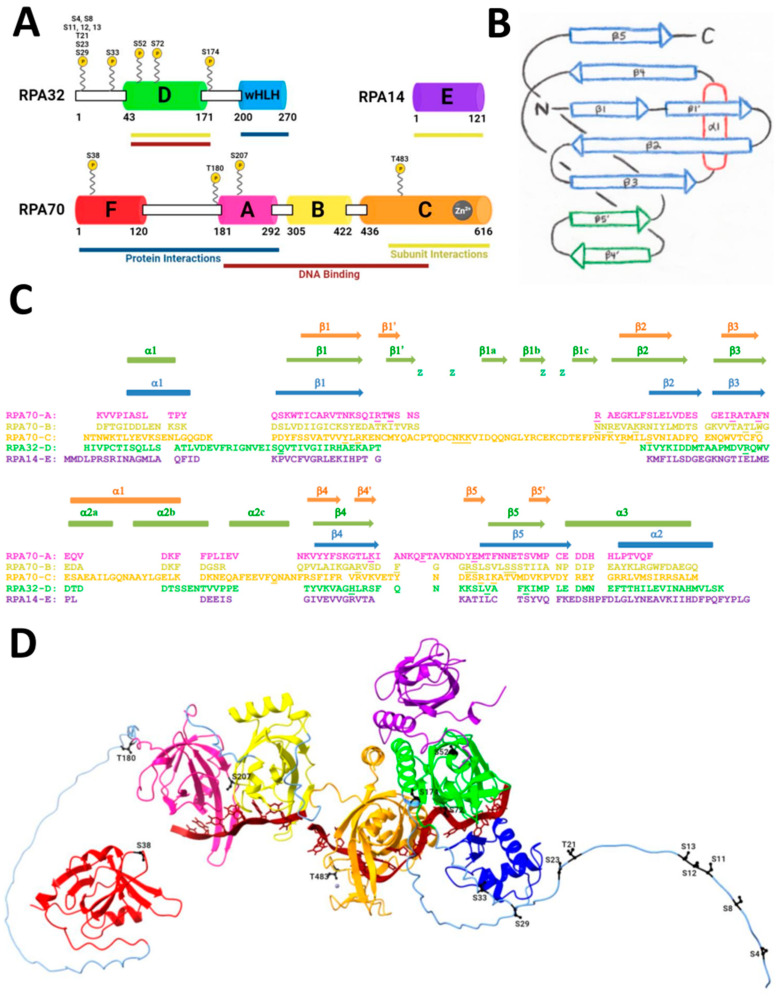
Figure 1.
Structure of RPA. (A) Domain diagram of RPA heterotrimer with domain functions and phosphorylation sites. Structured domains are colored and labeled A–F and wHLH. Unstructured domains are white rectangles with a black outline. Phosphorylation sites are labeled and shown with a yellow circle indicated by P. Protein interaction domains are underlined in navy blue. DNA binding domains are underlined in maroon. Subunit interactions that form the heterotrimeric core are underlined in dark yellow. (B) OB-fold diagram [66]. Arrows indicate the β-strands and an oval indicates the α-helices. The blue β-strands correspond to those that comprise the OB-fold. The L12 loop lies between β1′ and β2, and the L45 loop lies between β4′ and β5′. (C) Sequence and secondary structure alignment of domains A–E based on structure (updated from [53]). Orange secondary structure elements represent domains A and B, green elements represent domain C, and blue elements represent domains D and E. Lowercase z indicates the Cysteine residues in domain C that bind zinc. Residues in RPA70-A, RPA70-B, RPA70-C, and RPA32-D that bind to ssDNA are underlined. RPA32-D contains putative DNA binding residues that were determined through structural alignment of human and Ustilago maydis RPA. (D) AlphaFold predicted the structure of RPA with ssDNA. Domains are colored according to the domain diagram in A. The zinc in RPA70-C is shown as a gray ball. PIKK/CDK in G2 phase phosphorylation sites are black and labeled. The phosphorylation sites: in RPA70 are S38, T180, S207, and T483; in RPA32 are S4, S8, S11, S12, S13, T21, S23, S29, S33, S52, S72, S174. ssDNA, shown in maroon, was superimposed from 4GNX [67].