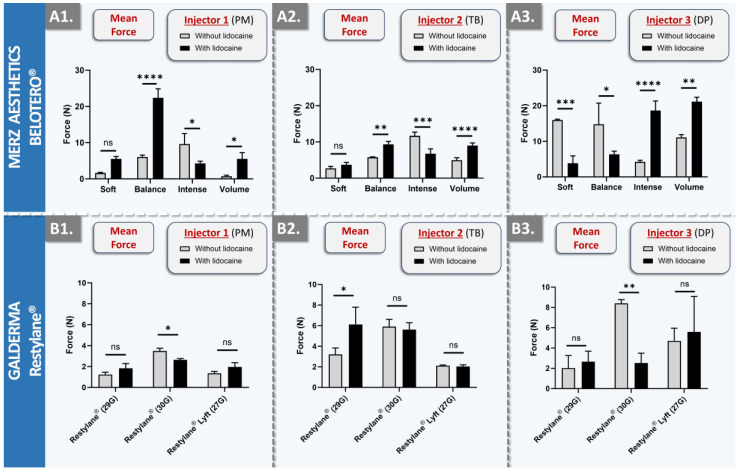
Figure 2.
Results of in vitro manual injectability studies for the assessment of inter-injector variability and quantification of the influence of lidocaine on product injectability. The quantitative measurements were performed using the SimSkin® cutaneous equivalent and the FlexiForce® dynamometric sensor. The injections were performed using a point-by-point administration method. (A1–A3) Comparison of mean injection forces for BELOTERO® products (i.e., with and without lidocaine) between the three injectors. (B1–B3) Comparison of mean injection forces for Restylane® products (i.e., with and without lidocaine) between the three injectors. Experiments were performed in triplicate, and results were presented as average values assorted to corresponding standard deviations as error bars. Statistically significant differences (i.e., * or p-value < 0.05), very significant differences (i.e., ** or 0.001 < p-value < 0.01), or extremely significant differences (i.e., *** or 0.0001 < p-value < 0.001; **** or p-value < 0.0001) were found between the average values. Detailed results of the statistical analyses are presented in Table S3. DP, Daniel Perrenoud; G, gauge; ns, non-significant; PM, Patrick Micheels; TB, Thierry Bezzola.