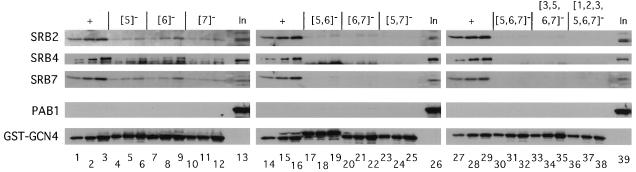
FIG. 5.
Additive effects of mutations in hydrophobic clusters 5 to 7 of the activation domain in GST-Gcn4p fusion proteins on binding of Srb2p, Srb4p, and Srb7p in yeast cell extracts. A fixed amount of yeast extract (containing 1,500 μg of protein) prepared from strain DPY213 expressing HA-yTAFII130 was incubated with three different amounts of bacterial extracts for each GST-Gcn4p fusion containing ca. 5, 10, and 20 μg of total bacterial protein and the appropriate amounts of a control bacterial extract lacking a GST fusion protein to bring the total amount of bacterial protein in each reaction mixture to 23 μg. GST-Gcn4p fusion proteins contained the wild-type Gcn4p activation domain (+) (lanes 1 to 3, 14 to 16, and 27 to 29) or mutant activation domains with substitutions in the hydrophobic clusters shown in brackets across the top. The GST fusion proteins were precipitated and subjected to immunoblot analysis with polyclonal antibodies against the proteins indicated to the left of each panel, exactly as described for Fig. 3. Lanes 13, 26, and 39 contain 1/20 of the input (In) amount of yeast extract employed in each binding reaction mixture.